The digital footprint of organizations has evolved and grown significantly over the past 10 years, now its important to not only protect just IP addresses and domains but also social media, payment platforms, and third-party services. Identifying risks like vulnerabilities, supply chain attacks, and credential leaks are crucial for organizational security.
The Cyberint team have analyzed 1000s of risks and threats and narrowed down the top 4 risks facing Latin America in 2024 and going into 2025.
The Verizon Data Breach Report showed that worldwide in 2019 and 2020 the second most common attack vector was stolen credentials. By 2021 to 2022 it was the most common attack vector. There are various methods of credential theft, including data breaches, malware infections, and social engineering:
The data breach is the primary method for credential leakage. Corporate networks are often compromised, leading to the theft and exfiltration of databases containing user credentials. In some instances, these databases contain hashed passwords, but in others, usernames and passwords are exposed in plain text.
High-Profile Examples
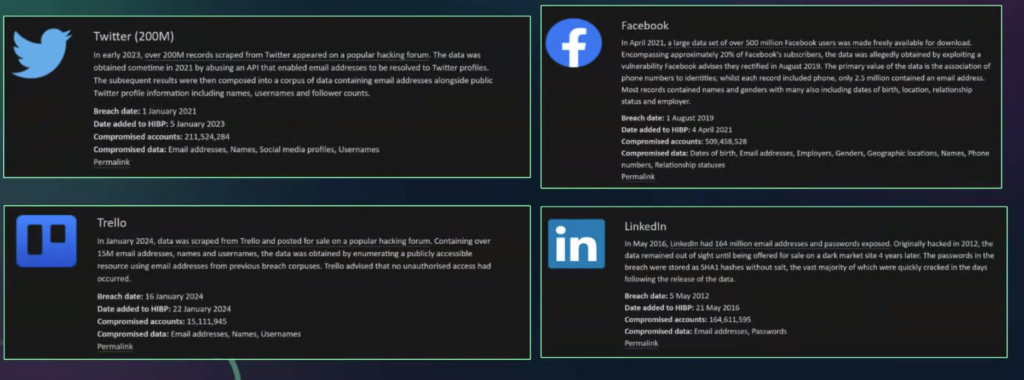
Examples of this include Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook. These examples underscored the severity and widespread impact of credential leaks on both individuals and organizations.
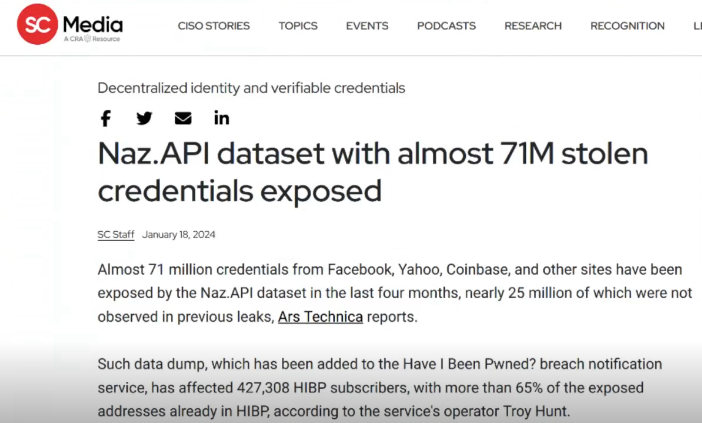
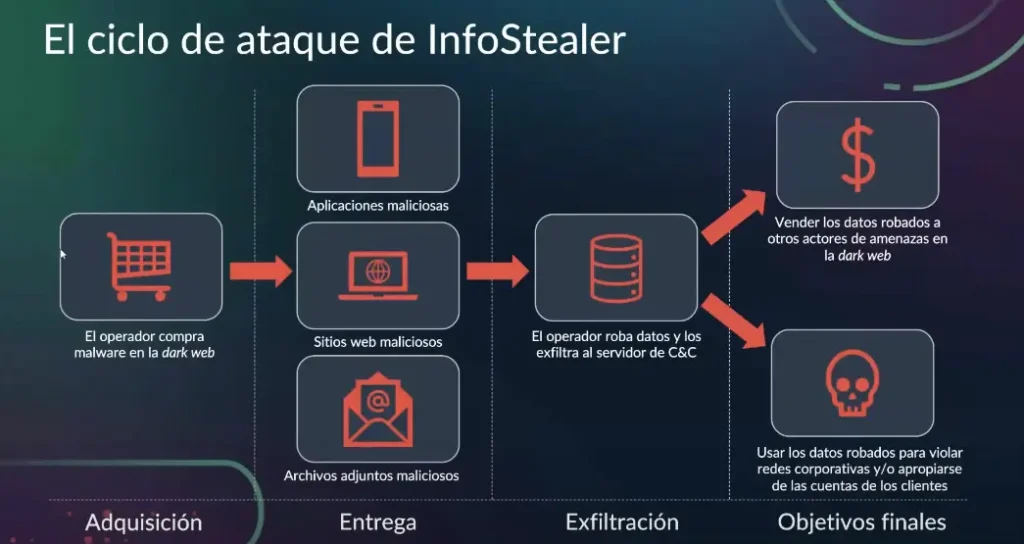
Another significant method is malware infections, particularly through info stealers and Remote Access Trojans (RATs). These types of malware are designed to collect credentials from infected devices and send them to servers controlled by threat actors, who then use or sell the stolen information.
Social engineering tactics, such as phishing and business email compromise (BEC) attacks deceive individuals into revealing their credentials by impersonating trusted entities or individuals through emails, messaging, ads or/and malicious websites.
To combat the risk of credential leakage, Cyberint recommends several strategies, including:
The IBM Threat Intelligence report (https://www.ibm.com/reports/threat-intelligence) lists Phishing among the top attack vectors in 2022-2023. Phishing’s effectiveness stems from its ability to impersonate trusted entities, thereby deceiving individuals into divulging sensitive information, such as login credentials. Tactics include, but are not limited to phishing, business email compromise (BEC), and vishing.
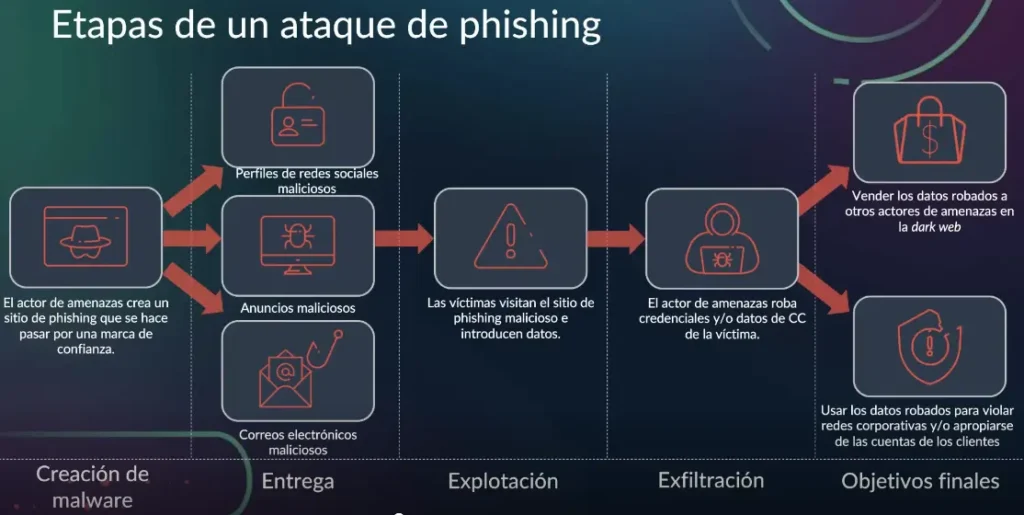
Phishing attacks are getting better and more misleading. Subdomains of malicious sites are easily made to look like a genuine page:
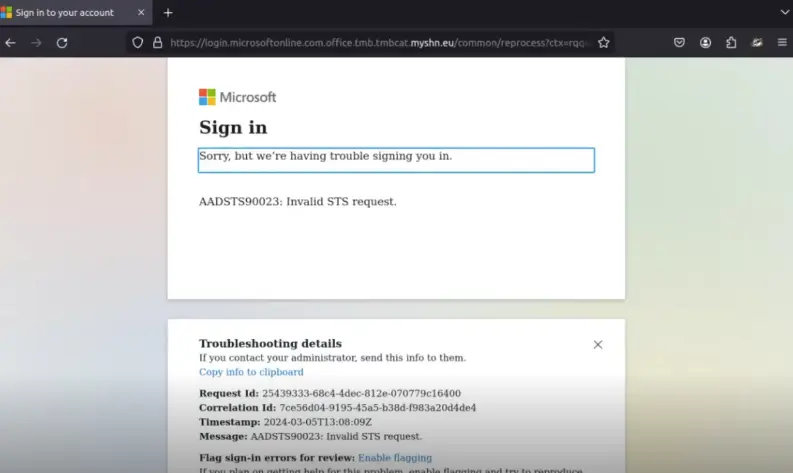
Social Engineering Tactics exploit human psychology to trick individuals into making security mistakes or giving away sensitive information and they are becomind harder to spot with the advent of AI.
To combat phishing and social engineering threats, Cyberint recommends several strategies. These include:
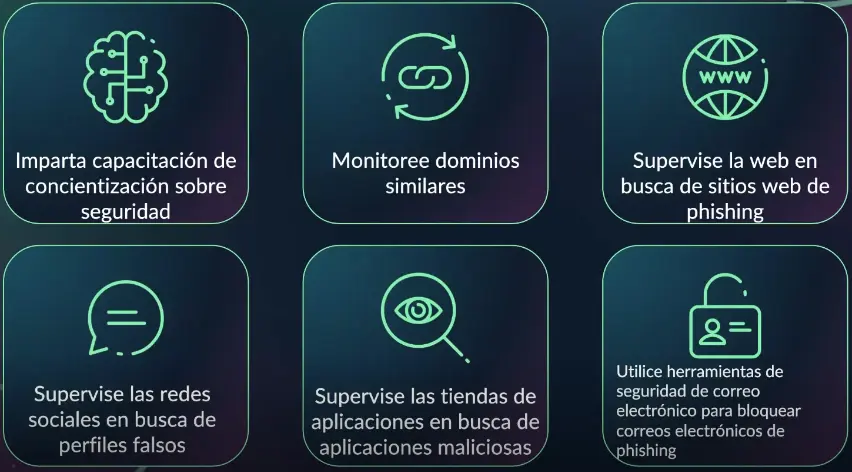
Continuous monitoring for phishing attacks, lookalike domains and social media patches is crucial in preventing these attacks.
MFA is a crucial security measure that adds an extra layer of protection beyond just a username and password. It’s recommended for enhancing security across various platforms and services. But, attackers can bypass MFA by the following methods:

Attackers hijack a session after the user has authenticated by stealing or using previously obtained session cookies, allowing them to bypass MFA without needing the user’s second factor.

Through phishing attacks, attackers deceive users into entering their MFA codes on a fake login page. The attackers then use these codes to gain unauthorized access.
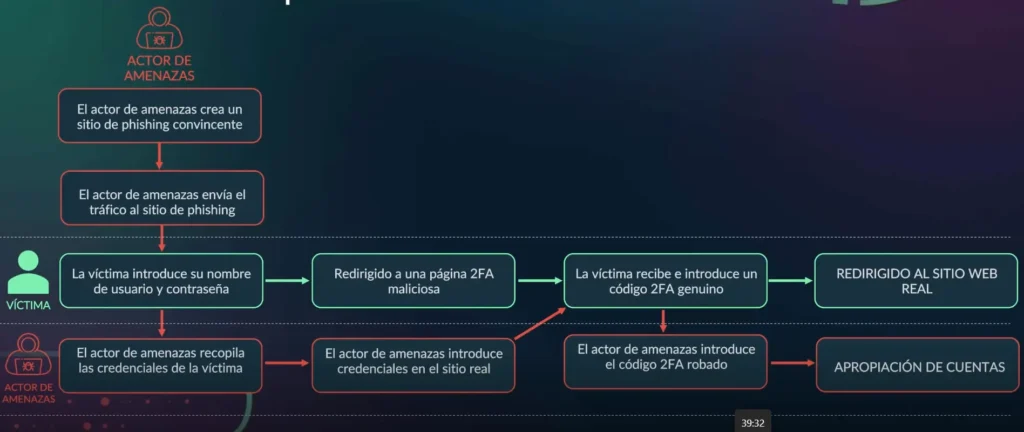
Attackers exploit push-based MFA by sending repeated push notifications to users. The users, overwhelmed by the constant notifications, may inadvertently approve an authentication request, granting the attacker access.
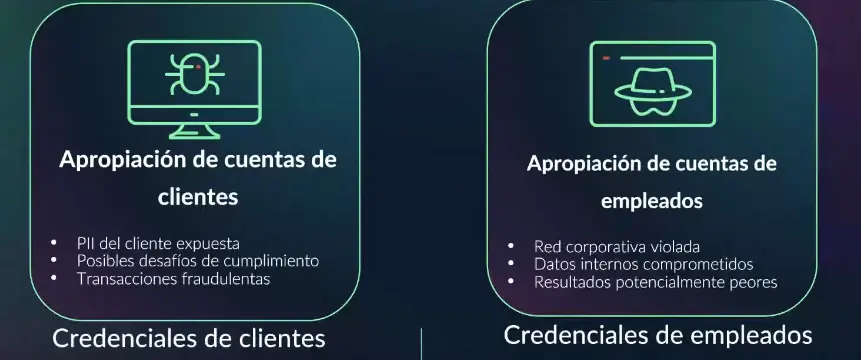
Cyberint detects and collected tens of thousands of sensitive cookies from multiple unique sources. Alongside the cookies file there is additional information about the infected host and the login pages, which also assist to identify the vulnerable company, those companies are in constant risk if no action is taken. Continuous monitoring of deep and dark web sources for these types of threats is very important.
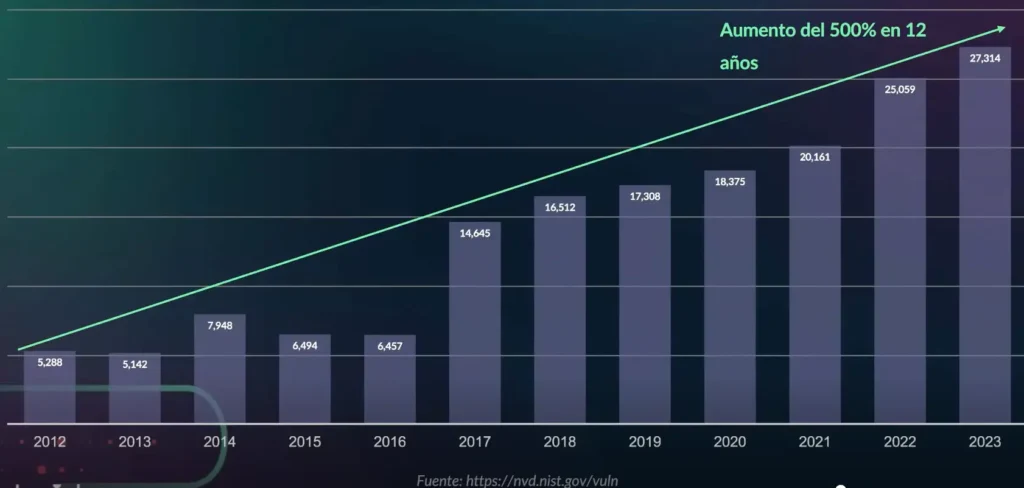
There’s been a significant increase in the number of CVEs detected over the years, with a notable rise in the last decade. This trend suggests a growing challenge in managing vulnerabilities.
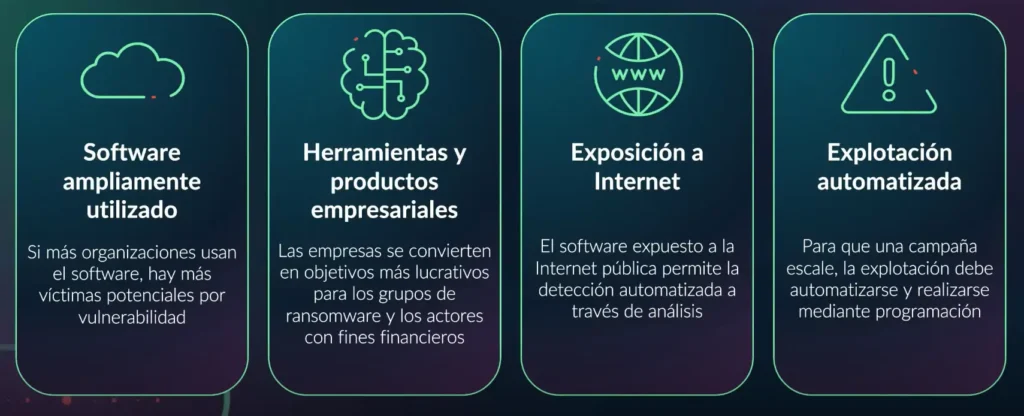
CVE exploitation remains a primary attack vector, with attackers increasingly targeting widely used software and technologies, including security technologies, to find vulnerabilities.
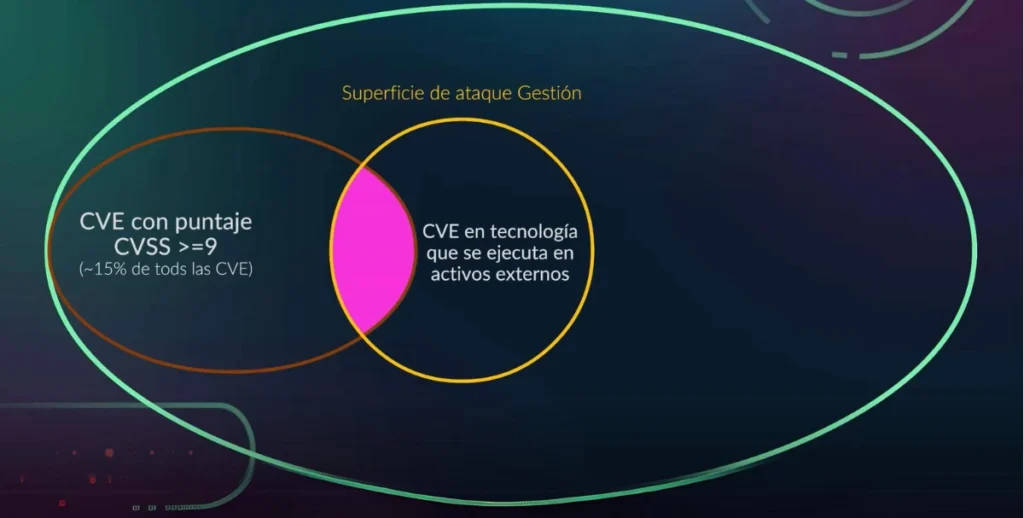
While many CVEs are documented, a smaller percentage (2-5%)are actively exploited in the real world. Therefore it’s important to focus on high-risk CVEs for mitigation efforts.
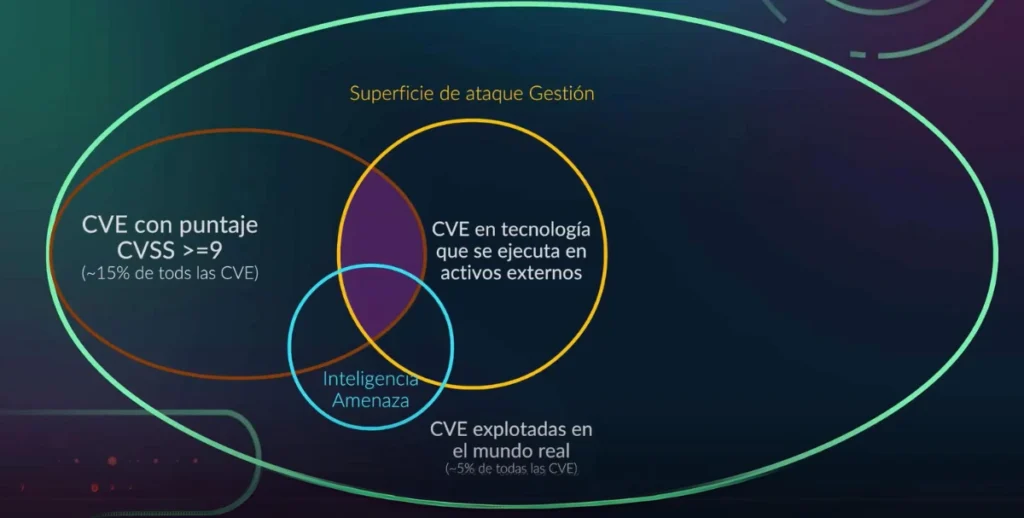
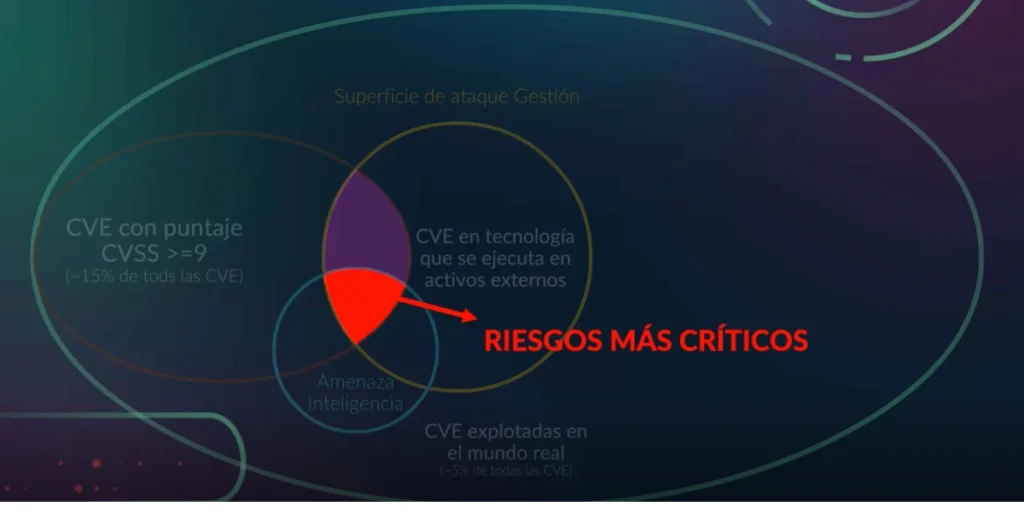
For an attack to scale, the exploitation process needs to be automated. This automation allows attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in widely used software and services more efficiently.
The threat landscape is dynamic and although these are the current threats it is important to stay on top of the changing threats. Cyberint strategic threat landscape dashboard can help you stay on top of trends in your industry and region.
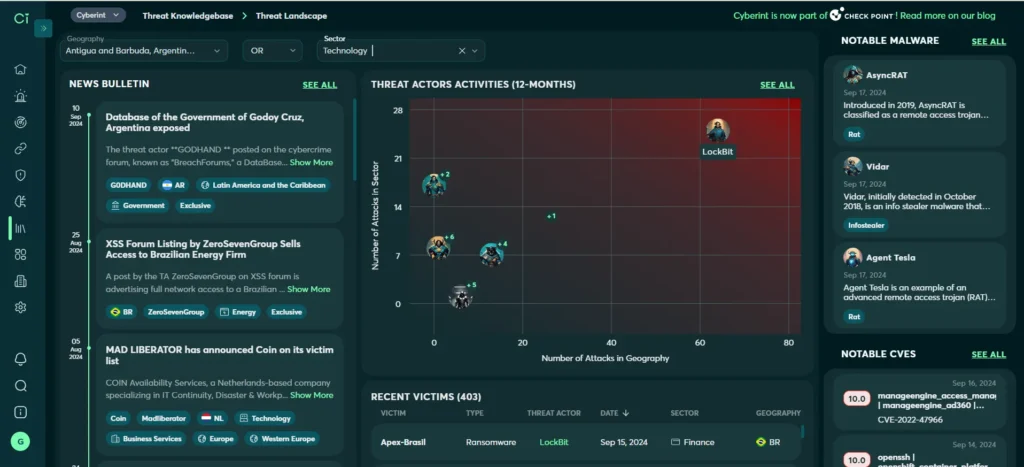
The Cyberint Attack Surface Monitoring module continuously discovers your organization’s digital footprint, creating a complete asset inventory and providing visibility on your Internet-facing digital assets. The ASM module then identifies security exposures, assesses the risk of each one, and assigns risk scores to simplify prioritization, accelerate remediation, and help you improve security posture.
Learn more about Cyberint offerings, including Digital Risk Protection, Threat Intelligence, Supply Chain Intelligence and more on a Demo.
Fill in your business email to start