


The UEFA League, alternatively known as Euro 2024, has officially started, marking a thrilling period for football fans worldwide. The unmatched enthusiasm for watching the matches, whether through digital screens or by experiencing the live vibe in the stadiums, has filled the air. However, this surge in excitement isn’t solely confined to sports fans but has also caught the attention of threat actors. These threat actors are exploiting the event’s anticipation to ramp up their nefarious activities.
As each match in the UEFA League emerges as an event of significant attention, the need for awareness about potential risks and effective mitigation strategies becomes paramount. Not just for individuals but corporations as well, understanding how to safeguard against these cyber threats is essential. This calls for a rigorous examination of the cybersecurity landscape surrounding events like Euro 2024.
In an effort to shed light on this pressing issue, Cyberint has embarked on an extensive surveillance campaign. By delving into the realms of the deep and dark web, monitoring conversations and activities on social media platforms, and analyzing open-source intelligence, Cyberint aims to capture a comprehensive view of the cyber threats associated with Euro 2024.
Such vulnerabilities present a tangible risk, potentially serving as gateways for threat actors to launch attacks. Moreover, the exposure of sensitive data is another critical issue, further complicating the cybersecurity challenges tied to Euro 2024.
Adding to the complexity, the Cyberint report delves into various attack vectors employed by threat actors. These range from phishing scams aimed at deceiving fans into revealing personal or financial information to more sophisticated methods that target the event’s infrastructure. By exploring these methods in detail, Cyberint aims to not only inform but also equip stakeholders with the knowledge needed to counteract these threats.
Each year, billions of compromised credentials appear online, either on the dark web, clear web, paste sites, or in data dumps shared by threat actors. These credentials are then used by threat actors for account takeover attacks, fraud, and data theft.
Stolen or infiltrated login details, accessed by unauthorized parties are called compromised credentials. Typically, compromised credentials include usernames, passwords, security questions, and other sensitive information used to verify a user’s identity and gain access to accounts and systems.
Credentials are often exposed with the help of credential harvesting malware, which infects the victim’s machine and sends user input logs, including harvested credentials, to the Command & Control (C&C) server operator.
Threat actors may use compromised UEFA customer credentials to perform fraudulent account activity (the so-called Account Takeover) on the customer’s behalf, including account ticket purchases and ticket transfer.
Furthermore, threat actors can steal sensitive personal information, impersonate the account owner, gain access to funds or payment cards as an entry point to defraud the owner’s contacts or other fraudulent schemes, etc.
Since the beginning of 2024, Cyberint has detected more than fifteen thousand UEFA customers’ credentials being exposed.

It is a lucrative market for threat actors who can steal credentials and sell them on the black market. In addition to already exposed credentials, Cyberint detected more than two thousand UEFA customers’ credentials that were up for sale on dark web marketplaces.
The fresher the compromised credentials, the higher the chance the threat actors can achieve their financial objective. However, credentials are rarely used by threat actors in “real-time.” Unless the credential is compromised in highly targeted attacks, threat actors require time to analyze the reams of data that they have captured. This process of filtration and extraction enables them to pull out ‘prime’ credentials either to sell on illegal marketplaces or use them for further exploitation.
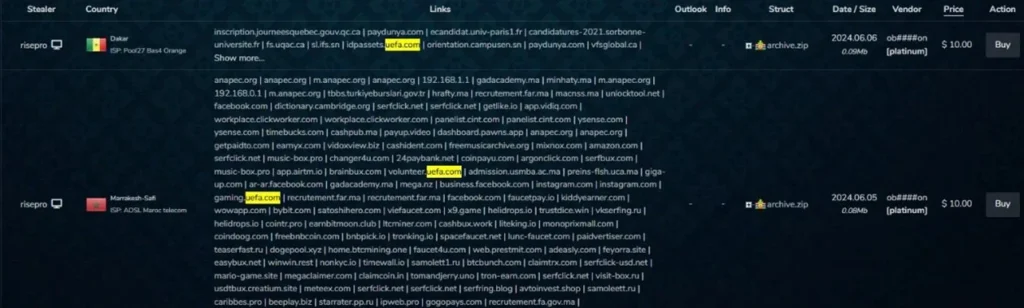
Exposed credentials can be very damaging, not only to the business’s brand reputation, but also have financial and even legal implications. Furthermore, it should be kept in mind that users will most likely blame the business for any damage that occurs through exposed credentials and account takeovers, blaming it on the company’s lack of security and fraud-prevention measures.
More information about compromised credentials can be found at Compromised Credentials: Tactics, Risks, Mitigation
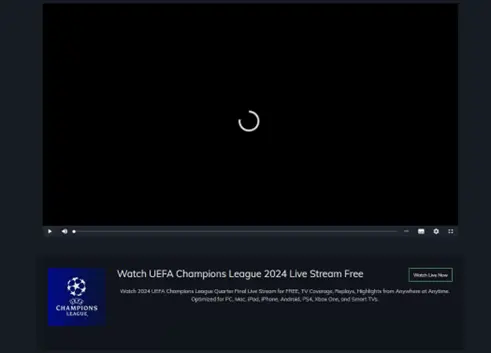
UEFA has sold the streaming rights for its tournaments to some of the most popular media networks. Since watching the games requires paying for broadcast network subscriptions, threat actors are luring people without cable or streaming subscriptions by creating illegal content sites claiming they will stream the games for free.
It is a known tactic for threat actors to create illegal content sites to attract film and TV enthusiasts by offering free movies. Still, their goal is to steal personal data by infecting users’ computers with malware.
When users click the link, their data can be compromised, or their devices can be infected with a virus. These sites may then hold the victim’s computer and network for ransom, demanding payment to unlock them. They could also gain control of a system and use it to commit fraud or spy on their victims. In some cases, simply visiting the site can infect your device – a drive-by download is a malware attack that can occur just by visiting a webpage.
Although some such sites’ agenda might be to broadcast the games for free (which results in income loss to UEFA), it is recommended to avoid such websites.
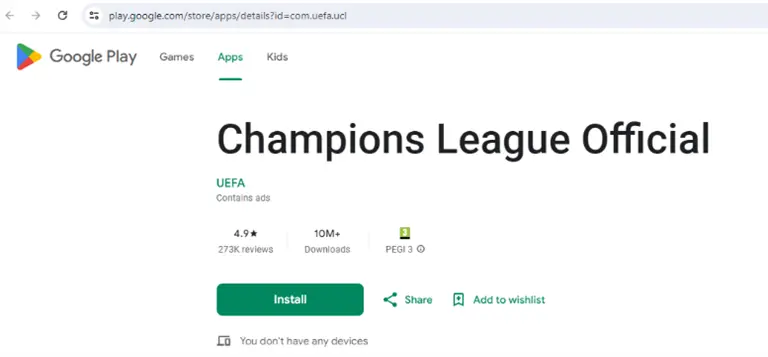
Mobile apps impersonating UEFA’s official app are publicly available for download on many third-party app stores.
Third-party app stores are considered less safe than official stores like Apple’s App Store or Google Play. Because they are not subjected to the same oversight as official app stores, anyone can upload apps without any supervision. Threat actors upload unauthorized apps to those stores, which are often products of brand abuse and might contain malicious elements, exposing users to malware and data breaches.
The apps use the company’s name and logo, targeting UEFA’s fans, customers, and volunteers.
When using an unofficial store, a good practice is to download the app and compare its hash to the company’s official app. However, the best practice is to download the app from the UEFA official site or only from authorized Google and App Stores.

Further reading material regarding malicious apps can be found on the Cyberint blog: Chapter 1: Android Malware Starters Pack
Heading to the Euro 2024 football games? Ensure Your Tickets are Real.
With the excitement building around Euro 2024, fans are securing their game tickets. The surge in demand for these game passes makes them a hot commodity, and unfortunately, this also opens opportunities for scammers looking to capitalize on the fervor.
The most common pitfall for eager fans is the allure of third-party ticket-selling websites. While these platforms can serve as a legitimate marketplace for ticket exchange—offering a second chance at tickets for those who missed the initial sales—they also pose a significant risk. The reason? Not every seller is looking to pass on tickets they can no longer use. Instead, some are looking to exploit fans’ enthusiasm by peddling fake or non-existent tickets.
But it doesn’t stop at third-party websites. Scammers have become increasingly sophisticated, reaching out through social media or setting up elaborate phishing websites designed to mimic legitimate ticket sellers. These efforts are all aimed at one thing: deceiving unsuspecting fans.

Another vector of ticket fraud is the ticket lottery. By simply filling in a few “harmless” details, you enter the lottery for a chance to earn free tickets. Threat actors use the provided details; they can either target the victims for scams such as phishing or sell the information to the highest bidder.
For safe ticket purchasing, buy tickets only from authorized sources like UEFA’s official website, promoters, or other reputable sites. Use secure payment platforms like PayPal for safety and refund options when buying from individuals. Prefer credit card payments for added protection and avoid direct bank or money transfers.
The Dark Web is a section of the Internet that search engines cannot index, and it can only be accessed using specialized software like the Tor browser. It is known for hosting both legal and illegal activities. Illegal activities include the sale of drugs, weapons, stolen data, and other contraband. Threat actors use the Dark Web to offer Malware-as-a-Service and sell stolen subscription credentials.
Read our blog explaining the dark web here
The Dark Web is not merely a realm of anonymity – it is a bustling hub offering a plethora of illicit offerings. Threat actors utilize the dark web in various ways, for example:
During Cyberint’s monitoring of the Dark Web, we have observed threat actor discussions related to UEFA, searches for sales accounts, offers of tickets for sale, cheap or free streaming services, UEFA compromised customer credentials for sale on dark web marketplaces, and more.

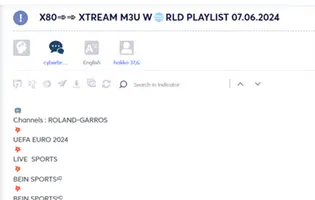
Finally, as it turned out, there are quite a few football fans among the threat actors. Not all their discussions are around illicit activities, some of them just wanna have fun.

Extending on the initial insights, Cyberint’s detailed examination of the cybersecurity landscape surrounding Euro 2024 highlights the significant rise in opportunities for threat actors to exploit. As Europe’s biggest football nations come together, celebrating a festival of sport, the flip side reveals an increasing threat landscape, where the enthusiasm and wide digital footprint of millions create a perfect storm for cyber-attacks.
Cyberint’s comprehensive report dives deeper into the methods and strategies employed by these threat actors, who are becoming ever more sophisticated in their approaches. Phishing campaigns, malware infections, and financial fraud are among the top concerns, with these entities often masquerading as official merchandise vendors, ticketing platforms, or even fan forums to execute their malicious intents. The increase of social engineering tactics, leveraging the event’s popularity, exposes fans and associated organizations to heightened risks.
Moreover, Cyberint research brings to light the critical importance of cybersecurity awareness and readiness. It emphasizes the necessity for continuous monitoring and intelligence sharing as instrumental in mitigating such threats. For individuals, this means being cautious of unsolicited communications, verifying the authenticity of websites and emails, and using secure payment methods when purchasing related merchandise or tickets online. Organizations, particularly those directly connected to the event, such as sponsors, broadcasters, and hospitality providers, are urged to strengthen their cybersecurity postures. This encompasses implementing advanced security protocols, conducting regular security assessments, and engaging in cybersecurity training for their staff.
In essence, the celebration of Euro 2024 should not be marred by the actions of opportunist threat actors. With thorough vigilance, informed decision-making, and concerted efforts toward cybersecurity, the football community can enjoy this spectacle while minimizing the risk of becoming victims of cybercrime.

Fill in your business email to start.
©1994–2026 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved.
Copyright | Privacy Policy | Cookie Settings | Get the Latest News
Fill in your business email to start


