Your brand is the image your customers have of your business; this is precisely what makes your brand into such a valuable asset.
It’s no surprise that brand presence is increasingly shifting into the digital realm. And while digital transformation brings with it a whole new world of possibilities, the digitization of the brand also introduces new risks. In the digital domain, malicious third parties can abuse intellectual property in a multitude of ways, often leading to far-reaching negative consequences for the organization’s bottom line.
The potential damage of a successful attack on a brand can be devastating, negatively affecting revenues and reputation.
Online brand protection is a necessity, and organizations are gearing up to protect their brand on all fronts. CMOs, CIOs, CISOs, and Heads of IT are working together to create a solid brand protection strategy that is capable of bolstering your brand’s defenses against digital threats.
Just like the online world itself, the threats in the digital realm are varied. It is important to understand the common threats in order to defend against them.
Brand impersonation happens when a third party impersonates a trusted brand in order to trick victims into responding and divulging personal, sensitive, or valuable information. Threat actors utilize multiple digital vectors for their attacks, including:
Social media: Most common types of brand impersonation attacks on social media channels include fake or compromised company employee accounts, often targeting the C-level management team. Another threat is the impersonation or hacking of corporate social media accounts.
Email attacks: Such attacks often include domain squatting or typosquatting to trick the recipient into believing that they are opening an email from a trusted source. Another type of attack includes compromising the company’s email accounts that are later used to send malicious emails on behalf of the employee.
Phishing websites: There are roughly 200,000 phishing sites created each month, and this number is growing steadily. Phishing websites imitate the brand’s look and feel in order to trick users into submitting their login information that later can be leveraged for malicious gain.
Customers trust organizations with their personal data and expect this data to be kept safe and secure. Data leaks cause significant damage to a brand’s reputation that can be difficult to recover from, as the recent SolarWinds leak (and countless others) clearly demonstrates.
Data leaks can occur for a number of reasons:
Ransomware attacks are one of the most popular types of cybercrime today. Last year alone, 2,354 American government entities, healthcare organizations and schools fell victim to ransomware attacks. The average ransomware payout swelled to $178,000 in the first half of 2020, up from $112,000 a year ago, making it one of the more lucrative schemes for cybercriminals to turn to.
Getting hit with a ransomware attack damages the brand in many ways – from interrupting operations and losing customers, to being hit with multi-million dollar fines for failing to protect customer data, to causing severe reputational damage that can be impossible to recover from.
The rapid proliferation of the internet created fertile ground for trademark abuse. Intellectual property infringements online can take many forms, including:
In a web defacement attack, threat actors breach a website in order to replace the content with their own messages. Such an attack can have lasting reputational damage to the brand. Below are some examples of major brand implications from website defacement:


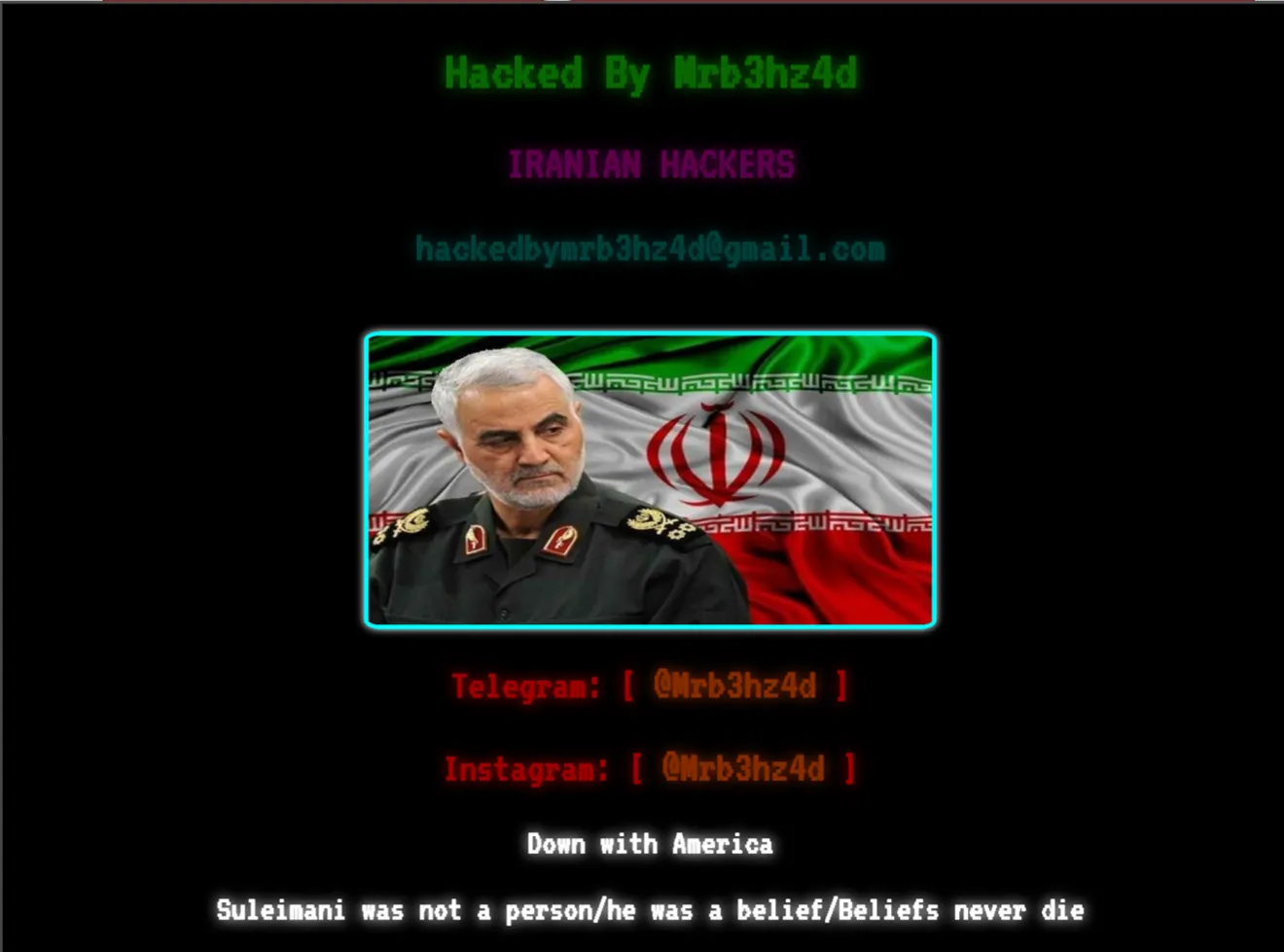
Cybersecurity Threat intelligence can help organizations build effective defense mechanisms and mitigate the risks that could damage their bottom line and reputation. Threat intelligence delivers the capability to defend more proactively, plan ahead, detect attacks in time and act on emerging threats before they turn into a breach.
Digital threat intelligence solutions sift through the Internet, Dark, and Deep web to gather data about emerging or existing threat actors and threats from a number of sources such as websites, forums, social media sites, or online marketplaces.
The primary purpose of a threat intelligence platform is to keep organizations informed of the risks of advanced persistent threats, zero-day threats and exploits, and how to protect against them. Detecting threats before they turn into breaches allows organizations to take a proactive approach to cyber risk.
The risks monitored by a cybersecurity threat intelligence solution include:
Threat intelligence data is then analyzed and filtered to produce threat intelligence feeds and management reports, as well as timely alerts on threats that can negatively affect the business.
As a leader in Threat Intelligence solutions, Cyberint has a dedicated team to respond to alerts as they come in and help initiate takedowns.
Threat intelligence approach to cybersecurity can proactively protect your organization against breaches, rather than waiting to react after an incident has occurred. Cyberint threat intelligence services can help your organization implement a proactive plan to identify possible threats to your brand.
Get in touch with us to see how we can help keep your brand safe
Fill in your business email to start