


Daniel is a seasoned cybersecurity product marketing professional with experience in cryptographic solutions, attack surface management, threat intelligence, and more.
Malware is not a new attack vector but, over the past few years, the Cyberint research team was observed a resurgence of this threat. In particular, a specific type of malware known as InfoStealers has become a serious risk.
This blog post will drill down on InfoStealers and discuss the lifecycle of an InfoStealer attack, from beginning to end.
Two developments in recent years have fueled the risk of InfoStealers: dark web marketplaces that make it easier than ever before to acquire InfoStealers and the massive increase in the number of potential targets—that is, Internet-connect devices—that bad actors can compromise.
As cyber crime as a whole has grown more sophisticated, the result is that very non-sophisticated attackers can join in. Malware-as-a-Service models make InfoStealers and other types of malware available on dark web markets for an affordable fee—just $50 to $300 per month. As the barrier to entry to acquiring and deploying malware gets lower, the risk stemming from this threat gets higher.
All of this is taking place while the number of devices in the average organization’s digital footprint is exploding. Work-from-home and bring-your-own-device policies are a major factor. IoT devices also play a large role. All of these devices are vulnerable to malware infections.
Once installed, InfoStealers begin gathering sensitive data from the compromised device, such as credentials, credit card details, crypto wallets, and cookies. Exposed credentials are a growing threat, as the sheer scale of credential dumps is hard to keep up with. The Cyberint research team discovers more than 17 Million sets of leaked credentials each and every month.
For a modest monthly fee, cybercriminals who don’t know how to write their own InfoStealer can simply pay to use one written by an expert. It works the same way as popular subscription services, like Spotify or Netflix. Anyone with a few hundred bucks worth of bitcoin can get started with a few clicks.
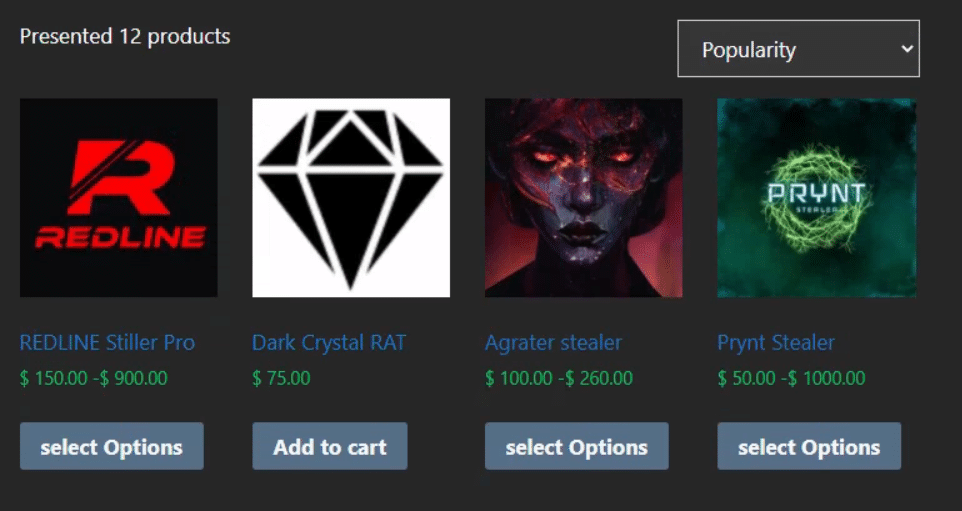
Dark web markets like the one shown above are surprisingly similar to legitimate e-commerce websites. The various vendors—in this case, the creators of the malware—market their products and try to highlight the benefits of their InfoStealer in comparison to other strains up for sale. Buyers leave reviews to rate the quality of the malware, the level of support they received, and other factors that may influence buying decisions. For cyber criminals, this is all just business as usual.
Once a threat actors has purchased an InfoStealer from a dark web marketplace, their next task is to spread the malware onto as many machines as possible. There are a few different techniques often used to deliver InfoStealers:
In recent months, threat actors have adopted a new tactic for spreading InfoStealers: paying for advertising on Google Ads and Facebook Ads to trick more people into downloading their malware. This threat was identified late last year and was so effective that the FBI’s IC3 issued a PSA on the topic.
Using paid ads to distribute malware is successful because it leverages the trust that people have in both the advertising platform and the brand that they are impersonating on the phishing site. If a user sees an ad after making a query in a search engine, they implicitly assume that it is safe to click because they trust the search engine. After clicking, the phishing site impersonates a third-party brand, which the user also knows and trusts, so they click to download the malware.
After the victim’s machine is infected with an InfoStealer, the malware begins taking sensitive data from a variety of services and applications. In general, InfoStealers target the following types of applications:
In particular, the specific services most commonly compromised by InfoStealers are shown below:
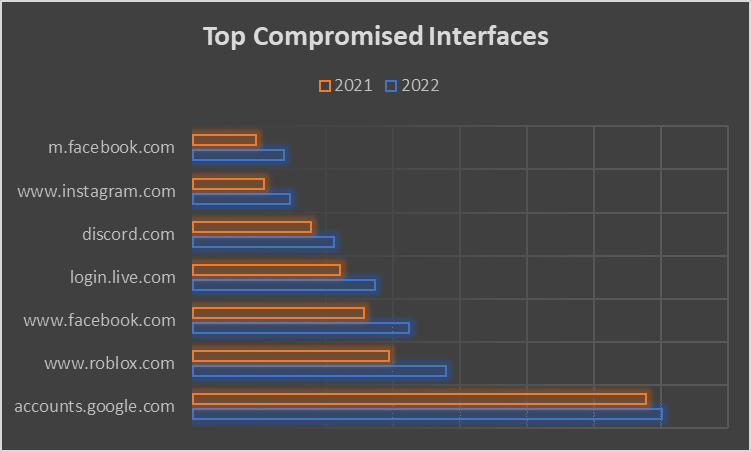
These services are targeted because they have enormous user-bases and they often store lots of sensitive data, making it easy for adversaries to scale up their attacks and harvest as much data as possible with the minimal effort required.
While it varies slightly from one strain of InfoStealer to the next, the type of data harvested from infected machines is relatively consistent across the board. Here are some examples of the data that InfoStealers grab:
After collecting all of this sensitive information, the malware sends the data from the infected machine back to the cybercriminals. The Cyberint research team has observed threat actors sending the data to intermediate locations, such as Telegram chats or Discord servers, rather than directly to a C&C server. This helps the bad actors to maintain anonymity and saves them the trouble of setting up and securing a command and control server.
Some security leaders underestimate the risk presented by compromised credentials because of multi-factor authentication solutions. While MFA is an excellent security control and should be implemented whenever possible, it is not a silver bullet. An alarming trend with InfoStealers is that they harvest data that can be used to bypass multi-factor authentication. This is true in two ways.
First, in many cases, users are only required to authenticate through multiple factors if the service does not recognize the user or after token expiration. This is often based on data visible server-side, such as the user’s IP address and whether or not the browser has a specific cookie for that service. Because InfoStealers take the cookies from the victim’s browser, bad actors can simply copy/paste the cookies into their own browser and use a VPN to fool the service and bypass MFA.
Second, if the victim has an active session with a web service, the threat actor can simply steal the session ID, for example by eavesdropping on the communication and hijacking the active session, thus bypassing all authentication requirements.
InfoStealers present a serious level of risk for enterprises. If a corporate device is infected, it becomes trivial for an adversary to take over the victim’s accounts and gain access to the corporate network. A number of enterprise solutions help mitigate this risk: anti-virus software, EDR agents, user behavior analytics, and so on.
However, even if an employee’s personal devices are infected, there is still a significant risk for the enterprise. If the organization uses a BYOD policy, there’s a good chance that the victim has logged into corporate accounts from the personal device—which means that the InfoStealer can take the usernames and passwords for access to these corporate accounts.
Additionally, because many people re-use username and password combos across multiple accounts, stealing the credentials for personal accounts and services may actually be the same thing as stealing the credentials for corporate accounts and services.
As the corporate attack surface expands and becomes murkier—extending far beyond the organization’s external IT infrastructure to include employee’s personal devices, accounts, and credentials—it’s essential to have visibility beyond corporate devices, servers, and domains.
Cyberint’s deep and dark web monitoring uncovers an average of more than 160,000 malware logs each month. Each malware log can contain the data stolen from hundreds or even thousands of infected devices. By mapping threat intelligence to the customer’s attack surface, Cyberint provides targeted, high-fidelity alerts that identify only the risks that matter to the organization.
For example, if an employee’s personal device is infected, but that employee has logged into web services using the username first.last@examplecustomer.com on the infected device, the Argos platform will automatically identify this in the malware log and generate an alert for the customer.
To see if your organization has sensitive credentials floating around the deep and dark web, request a free leaked credentials check from Cyberint.
The cyber threat landscape is always shifting. The growth of InfoStealers is just one of the latest risks that security teams need to be aware of and defend against.
To learn more about this threat, check out this report on InfoStealers from the Cyberint research team.
You can also register and join our upcoming webinar – Demystifying InfoStealers: An Update On Recent Trends.
Fill in your business email to start