

Emerging between late 2022 and the beginning of 2023, Cloak Ransomware is a new ransomware group. Despite its activities, the origins and organizational structure of the group remain unknown.
According to data from the group’s DLS (data leak site), Cloak has accessed 23 databases of small-medium businesses, selling 21 of them so far. Out of these, 21 victims paid the ransom and had their data deleted, 1 declined and 1 is still in negotiations, indicating a high payment rate of 91-96%.
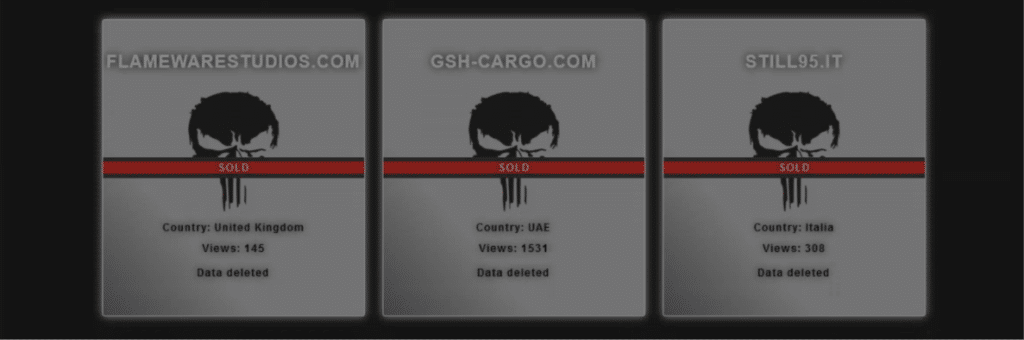
In case the victim refuses to pay the ransom (which has happened once), the victim’s data is published on the group’s DLS and can be freely downloaded by anyone (Figure 3). When the victim reported the incident to the police, Cloak published the data as a response.

IABs (Initial Access Brokers) are cyber threat actors who seek to procure access to your network and sell it to other threat actors. Buying the access allows the threat actor to gain permission, using the credentials given, to enter the sites and applications that the victim uses.
From the Cyberint Research Team’s analysis, we highly suspect that the threat actors behind Cloak ransomware are buying access from famous underground marketplaces such as the Russian Market from threat actors.
Cyberint’s Malware Log module was able to find compromised employee interfaces for sale that might have led to these attacks going back to May 2023, offered by campaigners of Lumma, Aurora, and Redline stealers, suggesting this as the initial step and primary attacking vector for gaining access to victims’ networks (Figure 4 & 5).
From the analysis of attacks posted on the DLS, the group mostly focuses on Europe, as Germany is the most targeted country (Figure 6).
The most impacted sectors include the medical industry, real estate, construction, information technology, the food industry, and manufacturing.
The Cloak Ransomware gang seems to be a rising threat in the cyber security field. According to the Cyberint Research team analysis, the group is buying IABs (Initial Access Brokers) on the Russian market to gain access to the victims’ network and, later on, infect it with their ransomware.
By looking at the victims’ distribution, attack vectors, and number of views for each post, we assume the group is financially motivated. There isn’t any connection between the targets and their locations, a behavior we notice in many ransomware groups, which indicates criminal activity with a primary motive of financial and personal gain.
Cyberint detects compromised credentials before they are even being sold on the dark markets so Cybersecurity teams can prevent the next ATO attack or ransomware attack, investigate, and further harden security so another leak is less likely to happen. Learn more about our protection here.

Fill in your business email to start


