The Cyberint Research Team work round the clock to unearth the latest threats to SMBs and enterprises. They are on top of the latest TTPs and monitor rising threat groups, malwares and trends.
The United States is a focal point for cyber threats, offering the highest potential gain to threat actors worldwide. Unquestionably, it remains the most targeted country worldwide.
Ransomware, poses a particularly severe threat to organizations globally, with the U.S. being its primary target. In light of these realities, this comprehensive threat landscape report aims to shed light on the specific cyber threats that the nation faces.
This report not only provides an overview of the prevailing cyber threats, but also delves into critical areas such as common threats, info stealers, hacktivists, and strategic risks such as supply chain attacks. Additionally, we will explore the potential risks associated with AI and ChatGPT in day-to-day activities.
Moreover, the report encompasses significant events from the first half of 2023 that warrant attention.
As mentioned, threat actors worldwide see great value in successful campaigns in the US.
When observing the communication channels of threat actors that are active in the US, we can see that most of their activity takes place on the Darknet and in underground marketplaces (Figure 1).
In addition, the second most active channel for threat actors is Telegram, followed by social media.
Among the most prevalent threats in the US are fraud, phishing, ransomware, info stealers, supply chain attacks, and hacktivism.
The U.S. is a global hub for technology, finance, and critical infrastructure, and therefore has become a prime target for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities.
Fraudulent schemes aimed at deceiving individuals and organizations are on the rise, including sophisticated phishing attacks. Ransomware attacks have wreaked havoc on businesses, encrypting their data until a ransom is paid.
Info stealers pose a significant risk, stealing personal and financial data for nefarious purposes. Supply chain attacks have emerged as a growing concern, targeting third-party vendors to infiltrate and compromise larger organizations.
Additionally, hacktivists leverage their skills to target government and corporate entities, aiming to promote their ideologies and demand accountability.
The breadth and complexity of these cyber threats in the U.S. demand constant vigilance and collaboration between public and private sectors to mitigate risks and safeguard against potential devastating consequences.
Fraud and phishing campaigns in the U.S. are two prevalent cyber threats that target individuals, businesses, and organizations. These campaigns aim to deceive and manipulate victims into revealing sensitive information, such as personal credentials, financial data, or login credentials.
Within the field of social engineering attacks, a common strategy involves employing a sense of urgency by using certain keywords such as ‘urgent,’ ‘important,’ ‘invoice,’ purchase,’ and related triggers. These keywords have become widely recognized by spam filters employed in email services, thereby diminishing their effectiveness in that domain. However, it is worth noting that SMS inboxes typically offer lower levels of protection compared to email services, and have various vulnerabilities that organizations need to be aware of.
Smishing attacks have been observed specifically targeting well-known U.S organizations such as Twilio and Cloudflare. In these cases, SMS messages were crafted to deceive employees into believing they needed immediate action or attention. Consequently, the employees were redirected to deceptive phishing interfaces, exposing them to potential security breaches.
While phishing vectors are the most common method for smishing, they can also be used to distribute malware without the victim’s knowledge. This is especially worrisome when corporate interfaces are present in private mobile devices, such as Microsoft Outlook or VPNs exposed to 0-day vulnerabilities.
According to the federal trade commission, the cost of fraud is equal to $8.8 billion in the United States. Out of the “fraudulent five” criteria, job posting spear phishing is in first place, followed by E-commerce fraud.
Cyberint has also observed an increase in job imposter fraud that targets candidates for positions in organizations. This fraud technique has become more prevalent, particularly with the rise in popularity of work-from-home positions. Threat actors exploit the online environment of remote work to deceive and target individuals seeking employment opportunities. Moreover, job imposter fraud involves impersonating legitimate employers or recruitment agencies to trick job seekers into providing personal information, financial details, or even making fraudulent payments. As a result, these negative experiences are indirectly associated with the targeted brand, which, in turn, negatively affects the perception of the company.
Cyberint has investigated several fraudulent job offers recently, which are usually distributed via social media. When victims interact with the job offer, the modus operandi is usually as follows:
Job Imposter fraud has also been observed to be involved with malware distribution where threat actors distribute infected files that are used to harvest credentials and other sensitive data from the victim’s machine.
The United States has one of the largest and most active online consumer bases in the world, making the country’s businesses and its consumer base an attractive target for fraudsters.
Moreover, it is also the most common type of fraud that businesses face, as the barrier to entry is considerably low, and the data is widely circulated and sold by various actors and stealer-malware operators.
Furthermore, the global nature of e-commerce presents challenges in jurisdiction and cross-border cooperation for law enforcement agencies. Fraudsters can operate from various countries outside of the U.S, making it difficult to track and apprehend them effectively.
With the rise of online transactions, e-commerce fraud has become a significant concern. Fraudsters exploit vulnerabilities in online payment systems, steal credit card information, and engage in various deceptive practices to defraud unsuspecting customers and businesses. This also includes using stolen PII information, stolen accounts or credit cards for fraudulent purchases that are sold on various chat platforms and forums. Moreover, there are also services that rely on stolen accounts; using them to fraudulently place orders on behalf of users and giving them a percentage discount.
The barrier of entry is considerably low, and the data is widely circulated and sold by various actors and stealer malware operators.
Phishing websites have emerged as a widely recognized risk, posing substantial dangers to businesses and individuals around the globe. As technology continues to evolve, the advent of AI tools has accelerated the creation of deceptive phishing websites, enabling threat actors to carry out sophisticated attacks with unprecedented ease.
Experienced threat actors are able to create custom made, sophisticated phishing kits that are easily accessible to less skilled individuals. This ease of deployment increases the overall threat landscape as more threat actors are now able to initiate and execute sophisticated phishing websites.
Strategic cyber threats in the U.S. refer to cyber attacks or campaigns that are carried out with specific objectives of achieving goals on a greater scale and with greater potential for damage. Strategic cyber threats often involve stealers, ransomware, hacktivism and supply chain attacks.
Information stealer malware, often classified as a Trojan, is primarily focused on obtaining data from infected computers and transmitting it to the threat actor.
It is designed to obtain sensitive data stored in the infected machine, including financial information, login credentials, Cookies and history, keystrokes, machine properties, and sensitive documents. This stolen information is packaged and sold as logs and may be exploited to gain unauthorized access to enterprise networks.
Infostealers are commonly sold on dark web forums and instant messaging platforms using the Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) business model, enabling individuals with limited resources or technical skills to deploy the malware and infiltrate networks.
Prices for various info stealer strains usually range from $100 to $200 per month or around $1,000 for a lifetime subscription. Threat actors then often sell the stolen logs in dark web marketplaces with prices ranging from $1 to $150, making them easily accessible to potential buyers. Any individual can quickly gain access to businesses by using the credentials and sensitive data sold in these marketplaces, which increases the associated risk.
“Cyberint has observed an increase of 329% in the stolen logs offered in these marketplaces in the past year.”
This trend aligns with the continuous growth of the information stealer industry as more threat actors and products enter the market. These stealers are evolving with additional features, such as the ability to function as loaders or Remote Access Tools (RATs), improved password reliability through support for two-factor authentication (2FA), and the use of covert communication channels with Command-and-Control servers (C2s).
Information stealers can be spread through a variety of methods, including malicious attachments in spam campaigns, websites infected with exploit kits, malvertising, free and pirated online software, phishing emails, network propagation, community-based platforms (e.g., Discord), and more.
Community-based platforms, such as Discord, attract a large number of users through social engineering. Threat actors can easily upload malicious files to Discord channels and share public links with others, even non-Discord users, making it a convenient method for distributing malware.
In addition, threat actors often adjust their social engineering techniques depending on the community they target, for example, in a designer-based community, threat actors will use patches to Photoshop and other Adobe products that will turn out to be malicious.
Threat actors use spam emails that mimic legitimate emails to lure users into unwittingly downloading malicious info stealer payloads.
Based on an analysis of recent campaigns, these communications include content related to urgent or pressing matters such as new orders, payment, purchase orders and quotations, as well as the apparent reuse of prior legitimate email threads that include contact details for and mimic an unwitting third party. Given the nature of the email lure, targeted recipients will likely include those working within Business Administration, Finance, and Sales teams. Furthermore, the compromise of one organization could lead to legitimate email accounts being abused to send effective lures to other organizations.
Recently, the Cyberint research team has noticed a growing trend among threat actors who favor utilizing paid advertising on platforms like Google and Facebook.
This seems to trick more people into downloading the malware, as they assume it is a legitimate and verified advertisement.
These campaigns revolve around popular services and events such as ChatGPT and 4th of July sales.
Information stealer malware presents a significant threat to both computers and mobile devices and can effectively target a diverse range of operating systems. For example, Atomic macOS Stealer (AMOS) exclusively focuses on Macs to extract sensitive information; ThirdEye Infostealer, which specifically targets Windows devices; and SharkBot Stealer, which targets Android devices.
The widespread nature of infostealer spreading methods and their goal of targeting as many victims as possible, presents a universal threat that can impact all sectors and regions without singling out any specific industry or geographic area.
Cyberint’s analysis of logs from the collection of Argos infected devices for 2023 shows that the United States ranks sixth globally in the rate of infected machines (Figure 4) with 8.09% of victims.
As for the most targeted platforms, it seems that google.com, facebook.com and roblox.com lead.
Regarding email accounts, unsurprisingly, Gmail is the most compromised email account, followed by Hotmail and Yahoo.

Fill in your business email to start.
Through the analysis of the Argos malware log collection and dark-web chatter, it became evident that certain info stealer families enjoy more popularity than others.
The popularity of certain info stealer families over others can be attributed to a variety of factors. However, the primary reasons for their popularity are their affordability, ease of purchase and operation, high success rates, and positive public perception.
Extensive analysis of popular info stealer families in both the United States and worldwide consistently identifies the same top five families.
Although new info stealer families emerge every day, the top families that are used by most threat actors are Redline, Aurora, Raccoon, Vidar, and Mystery.
The RedLine info stealer, first spotted in 2020, has maintained its position as the most popular info stealer since the beginning of the year, with 51.22% of the infected machines demonstrating its enduring appeal and continued usage by threat actors.
RedLine employs multiple distribution methods, including compromised software downloads, phishing attacks, and drive-by downloads. This powerful data collection tool is capable of extracting login credentials from a wide range of sources, such as web browsers, FTP clients, email apps, instant messaging clients, and more. It can also gather authentication cookies and card numbers stored in browsers, chat logs, local files, and even cryptocurrency wallet databases.
The RedLine info stealer is available for purchase on underground forums, either as a standalone product with prices ranging from $100 to $150 or as a subscription service priced at $100 per month.
The RedLine info stealer stands out due to its user-friendly interface, consistent patching, and high level of maintenance. These features make it highly attractive to threat actors, potentially contributing to its continued popularity as one of the most widely used info stealers.
Although considered relatively new in the market, only emerging in 2022, Aurora Stealer continues to gain popularity among threat actors, primarily due to its effective evasion techniques that help it avoid detection, particularly through advanced anti-VM (virtual machine) methods. This versatile botnet is designed to steal data and establish remote access to compromised systems. The distribution methods employed by the threat actors operating Aurora Stealer vary, including phishing pages that mimic popular applications, fake cracked software download websites, and even YouTube videos.
Once installed on infected machines, Aurora Stealer is capable of extracting various types of data from web browsers, including login credentials and credit card numbers. It can also target browser extensions, including cryptocurrency wallets, as well as applications like Telegram. Additionally, Aurora Stealer can load and execute additional malicious payloads on compromised systems.
Ranked in third place, Raccoon Stealer is a widely recognized info stealer known for its effectiveness in stealing sensitive and confidential information, including login credentials, credit card details, cryptocurrency wallets, Telegram data, and browser information. Raccoon Stealer emerged in 2019, and when compared to other stealers, demonstrates its capability to target a wide range of applications, allowing threat actors to access valuable information.
Raccoon Stealer can be readily obtained on underground forums at an average price range of $75 per week or $200 per month.
During H1 2023, Cyberint’s analysis of the Argos Malware Logs collection revealed that out of a total of 7,209,051 machines identified, 1,150,872 (16%) were corporate-related machines (work machines). Among these corporate machines, 90,348, approximately 9%, were found to have credentials for critical and sensitive platforms.
The risks posed by info stealers in enterprise environments are substantial. These malicious stealers can compromise sensitive data, including personally identifiable information (PII), financial information, and confidential business data, leading to potential legal and financial consequences.
Ransomware groups often employ information stealers or logs obtained from marketplaces. These groups specifically target info stealer logs to acquire important credentials, such as those used for remote desktop protocol (RDP) or virtual private networks (VPNs). With the stolen information from info stealer logs, ransomware groups can exploit compromised systems or networks more effectively. This may involve utilizing the obtained credentials to gain unauthorized access, extract sensitive data, or carry out specific targeted attacks.
An illustrative instance of this is the Lapsus attack on Uber, wherein the Lapsus group acquired an Uber employee’s credentials from a dark web marketplace. Lapsus utilized these credentials to gain access to Uber’s network and proceeded to communicate with the employee through WhatsApp, impersonating a member of Uber’s security team in order to bypass the obstacle of multi-factor authentication (MFA).
As a consequence of this attack, Uber experienced significant repercussions, including the unauthorized access to sensitive data by the threat actors, and a substantial blow to their reputation.
Even if an employee’s personal device is infected, it poses a significant threat to the organization if the employee has accessed corporate interfaces from their personal computer. Moreover, the practice of reusing username and password combinations across multiple accounts exacerbates the risk, as stealing credentials for personal accounts can inadvertently grant unauthorized access to corporate resources.
Supply chain attacks represent an evolving and increasingly sophisticated type of cyber threat. These attacks specifically target the intricate network of relationships between organizations, their suppliers, vendors, and third-party service providers. Exploiting vulnerabilities that arise from the interconnected nature of digital supply chains, which often span multiple organizations, systems, and geographic locations, malicious actors have devised methods to compromise trusted components or software within the supply chain.
This infiltration enables them to bypass traditional security defenses and catch their victims off guard. Given our growing reliance on global, interconnected digital supply chains, comprehending the risks and implications of supply chain attacks is vital to maintaining security and resilience.
While supply chain attacks are often associated with nation-state-sponsored groups involved in cyber espionage or critical infrastructure disruption, it is crucial to acknowledge that recent instances of supply chain attacks are not limited to these groups alone. Financially motivated cybercriminals and hacktivist collectives have also adopted this attack vector to accomplish their objectives. Exploiting vulnerabilities within supply chain vendors, these malicious actors infiltrate targeted organizations, distribute malware, and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
As we have already witnessed, several supply chain attacks have caused massive damage to organizations in the past. In 2023, high-profile recent supply chain campaigns included the 3CX, Applied Materials, and the MOVEit campaign.
In March, a significant incident, known as the 3CX supply chain attack, attracted attention to the integrity and security of the 3CX software supply chain. This attack specifically targeted the Windows and macOS desktop apps, raising concerns about their compromised state. The attackers achieved this by including a malicious library file within the apps, which, upon execution, downloaded an encrypted file containing Command & Control instructions. Consequently, the attackers gained unauthorized access to the victim’s environment, enabling them to carry out malicious activities.
What is particularly concerning is that the malicious versions of the apps were signed with valid 3CX certificates, indicating a potential compromise of the company’s build environment. As a result, apps that were tampered with were distributed directly from 3CX’s official download servers. This emphasizes the vulnerability of software supply chains, as even a seemingly minor breach can have extensive ramifications for customers who place their trust in and reliance on the software.
Moreover, this attack is linked to the North Korean state-sponsored APT Lazarus Group, showcasing the growing sophistication and persistence of threat actors targeting supply chains to infiltrate organizations and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
During February, a recent cyber attack on a business partner of semiconductor company Applied Materials disrupted shipments and was estimated to result in a Q1 2023 cost of $250 million. Although the specific partner affected by the attack has not been disclosed by Applied Materials, speculation points towards industrial equipment supplier MKS Instruments as the potential breach point. This suspicion arises from MKS Instruments announcing a ransomware attack on February 3 and subsequently rescheduling their fourth-quarter earnings call.
Applied Materials referred to the targeted company as a “major” supplier, and MKS Instruments was still in the process of recovering from the attack. The incident primarily impacted their Vacuum Solutions and Photonics Solutions divisions, causing delays in the processing and shipping of orders.
The ongoing MOVEit campaign continues to impact organizations worldwide, claiming new victims daily.
This extensive campaign serves as a prime example of the far-reaching consequences of a supply chain attack, affecting numerous companies globally.
MOVEit is managed file transfer (MFT) software widely used in healthcare, finance, technology, and government sectors. It employs secure File Transfer Protocols and encryption to facilitate safe data transfers within teams, departments, and organizations.
However, the MOVEit campaign exposed several critical vulnerabilities that, when exploited successfully, enable remote code execution and data breaches.
Interestingly, the Cl0p ransomware group had prior knowledge of the MOVEit vulnerability even before it became public. Evidence suggests that they have been exploiting this weakness since 2021 and were observed attempting to extract data from compromised MOVEit servers in April 2022.
At present, Cl0p has targeted more than 342 victims affected by the MOVEit vulnerability, with 225 of them located in the United States. The American victims come from diverse sectors, including finance, education, technology and software, energy, retail, healthcare, IT, law, insurance, investment, airlines, and even government services. This highlights the fact that no industry is exempt from supply chain attacks, and such incidents can occur anywhere, affecting companies of all sizes, from small to large. Notably, they have successfully targeted prominent American companies such as Norton, EY, and Zellis.
As we can see, supply chain attacks may have devastating results that echo through our threat landscape for the long term, and this is the best scenario possible for threat actors, as one successful compromise can lead to hundreds and even thousands of victims.
The increasing reliance on technology and interconnected systems in the supply chain has given rise to significant concern. Cybercriminals and nation-state actors often exploit vulnerabilities in supply chain networks to gain unauthorized access, disrupt operations, steal sensitive information, or compromise the integrity of products. These attacks can occur at any point along the supply chain, from suppliers and logistics providers to manufacturers and retailers.
The United States faces a constant and evolving risk of cyberattacks that target the supply chain, posing serious consequences for businesses, consumers, and national security. Supply chain attacks in the United States have a significantly greater impact than in other countries due to several factors that make it more attractive to threat actors.
First, the United States relies heavily on global supply chains and outsourcing. While outsourcing can provide cost-effective solutions, it introduces complexities in ensuring the integrity of the supply chain. The inclusion of foreign suppliers and manufacturing facilities can create vulnerabilities that threat actors may exploit. Given the global nature of supply chains, even an attack originating from abroad can easily infiltrate the U.S. network, making it harder to detect and mitigate.
In addition, the United States is a major economic power. The interconnectedness and complexity of the U.S. supply chain make it an attractive target for threat actors. The extensive network of suppliers, vendors, and contractors increases the potential attack surface and amplifies the consequences of a breach.
Many of the world’s leading technology companies are based in the US. These organizations often serve as key suppliers for various sectors, so compromising their products or services can have a cascading effect on countless downstream entities. A successful supply chain attack on a prominent US-based technology provider can potentially impact a wide range of critical infrastructures, government agencies, financial institutions, and businesses.

Ransomware might be the most popular threat to organizations worldwide.
While the US is the sixth most targeted country for info stealers, Ransomware is a whole different story. While the infostealers threat is based on the masses, ransomware is based on opportunity.
This leads to the US being the number one targeted country in the world, with 49% of all ransomware cases worldwide in H1 2023 taking place in the US.
As mentioned, the US is the number one targeted country by ransomware groups, followed by the UK and Canada.
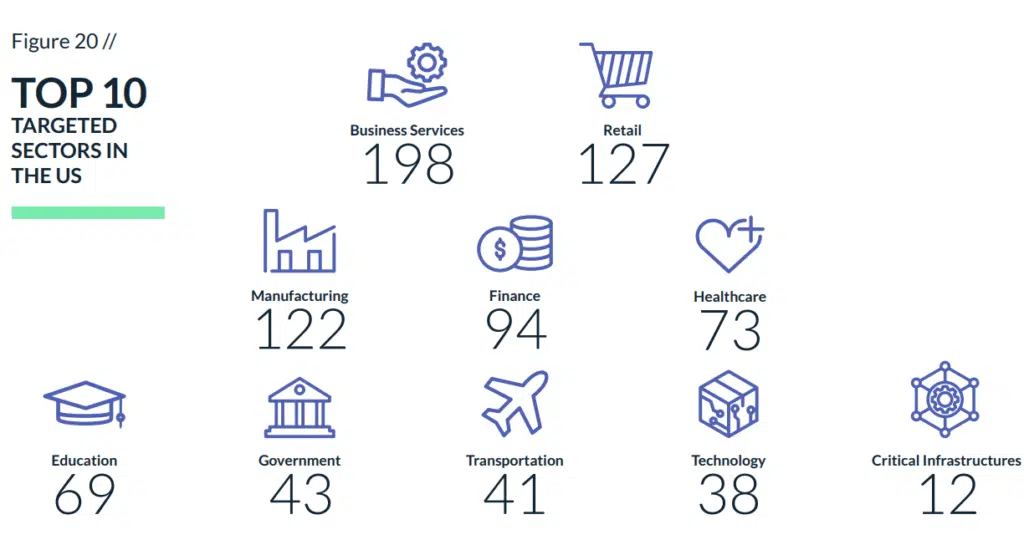
The most targeted sector in the US is business services, followed by retail and manufacturing sectors, respectively.
When observing the families that are responsible for most US cases, we find LockBit3.0, ALPHV and Clop.
LockBit3.0 stands as an experienced entity within the ransomware industry, demonstrating unwavering performance. Its primary modus operandi centers around employing social engineering tactics, including phishing, malspam, and the practice of bribing employees to willingly grant access.
Furthermore, we have observed instances where LockBit3.0 leverages and exploits vulnerabilities to gain initial access.
The group primarily targets the business services, retail, and manufacturing sectors.
ALPHV/BlackCat is a well-established crime organization that traces its roots back to the Darkside group, which was responsible for the notable Colonial Pipeline incident. After rebranding as BlackBatter, they have now adopted the name ALPHV/BlackCat.
The group and its affiliated members employ a range of tactics in their operations. They exploit vulnerabilities, carry out phishing campaigns, and leverage the services of malware-as-a-service providers like IcedID to execute their malicious payloads.
Similar to many other ransomware groups, ALPHV primarily focuses on targeting the business services sector. However, they also show significant interest in the retail and finance sectors, seeking out potential victims in these industries.
Cl0p is another veteran ransomware group we’ve become used to seeing in our threat landscape, especially in the US.
Unlike the ALPHV and LockBit3.0, Cl0p focuses most of its efforts on discovering and exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities. This leads to inconsistency in the group’s activity, although once they find a vulnerability they can utilize, it usually leads to massive campaigns with lethal results for their victims.
Great examples of campaigns Cl0p was involved in this year was the PaperCut campaign and the more recent and popular MOVEit campaign.
As we all know, Ransomware attacks have a significant impact on organizations. As the U.S. economy is one of, if not the, most thriving economy in the world, it also draws the attention of ransomware groups that seek to cause as much damage as possible in order to have the most leverage over the most successful companies in the world.
Among the many ways a ransomware attack can impact an organization, the most obvious is financial loses. Ransomware attacks can result in substantial financial losses for companies. This includes not only the ransom demanded, but also the costs associated with incident response, investigation, system restoration, and potential legal actions. The financial burden can be particularly challenging for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that may lack the resources to quickly recover from an attack.
Another way a ransomware attack can impact an organization is through operational disruption. Significant disruption to a company’s operations or critical systems, rendering them inaccessible and interrupting day-to-day business processes, can lead to downtime, delayed deliveries or services, loss of productivity, and customer dissatisfaction. The longer the disruption lasts, the more severe the impact on revenue and customer relationships.
Another heavy impact is data loss, which includes loss of sensitive business data, customer information, intellectual property, and trade secrets. Such data breaches can have legal and regulatory implications, damage customer trust, and expose the company to lawsuits and financial penalties.
Although it is hard to judge a company that is hit by ransomware, reputational damage is another way ransomware attacks can affect the victim. Ransomware attacks can inflict significant reputational damage on companies. A tarnished reputation can result in a loss of customers, diminished brand value, and difficulty in attracting new business opportunities. Rebuilding trust and restoring reputation can take considerable time and effort.
There is extensive debate about whether a victim should or shouldn’t pay the ransom.
Other than the ethical decision the companies need to make, in the U.S. regulations make things a bit more difficult as it is currently illegal to pay ransom.
This situation makes things much more complicated given the fact that once an organization has been compromised, its only goal is retrieving the stolen data and encryption key, and getting back on track.
In the aftermath of a ransomware attack, organizations may face investigations and potential penalties for non-compliance with these regulations. Industries such as healthcare and finance, which handle sensitive personal and financial information, are particularly vulnerable to such consequences.
As mentioned, almost half of the ransomware cases target the US. When analyzing ransomware attacks over the years, we can see that the U.S. is the land of opportunity for ransomware as well.
The U.S. has the world’s largest economy, with numerous businesses and organizations that can potentially pay significant ransom amounts. Targeting entities in the U.S. allows ransomware groups to maximize their financial gains – this is one of the main interest points for ransomware groups in their reconnaissance phase.
In addition, the U.S. has a highly developed digital infrastructure and widespread connectivity, making it an attractive target for cybercriminals. The extensive use of technology, internet connectivity, and reliance on digital systems create a larger attack surface for ransomware groups to exploit.
High numbers of technological innovation companies is another factor that draws ransomware groups to the U.S. given the many companies at the forefront of industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. These sectors often possess valuable intellectual property, sensitive data, and financial resources, making them lucrative targets for ransomware attacks.
In addition to the regulations we mentioned above, the U.S. has a regulatory framework that mandates reporting and disclosure of data breaches, including ransomware incidents. This transparency makes it easier to track and publicize attacks, which can sometimes attract more attention from ransomware groups seeking notoriety or seeking to maximize their leverage in negotiations.
Hacktivists leverage their hacking skills and tools to promote socio-political agendas, challenge authority, and disrupt systems or organizations they perceive as oppressive or unjust.
Unlike other cybercrime entities driven by financial gain or espionage, hacktivists operate with the intention of causing disruption, raising awareness, and promoting their ideological beliefs.
Since disruption and destruction are their favorite gain, these groups often target infrastructures, energy and government entities using techniques such as DDoS, website defacements and data breaches.
The pro-Russian hacktivist group called KillNet has recently emerged as the claimant behind a series of large-scale distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks targeting numerous major airports in the United States. These attacks have had severe consequences, rendering the affected airport websites completely inaccessible to users.
KillNet’s modus operandi involves overwhelming the servers hosting these airport websites with requests. The sheer volume of these malicious requests places an immense strain on the servers, effectively paralyzing their functionality. As a result, travelers and visitors attempting to access these websites have been met with frustrating and unresponsive pages.
The disruptive nature of KillNet’s actions has introduced significant challenges and hardships to both airport authorities and the traveling public. Like most hacktivist groups, KillNet published the victims on their Telegram channel.
The anonymous faction, SiegedSec, is well known for its campaigns against Western countries, especially the US. The group enjoys targeting high-profile companies and, earlier this year also targeted Atlassian.
As mentioned, many hacktivists groups target entities that are involved with conflicts of various kinds.
In this case, the group targeted the Texas Forth Worth government website claiming that Texas bans affirming care for the LGBTQ community.
The group was able to compromise the website and leaked roughly 500k stolen files.
Anonymous Sudan refers to a collective of hacktivists who are driven by religious and political motivations. Since January, they have been engaging in Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks against Western countries, specifically targeting organizations and critical infrastructure.
Recently, the group declared war against all Western countries. The US is one of their main targets, and they targeted Microsoft twice: once through a DDoS on the Outlook services, and the second claiming they were able to compromise and acquire 30 million Microsoft accounts.
Another American company that was targeted by Anonymous Sudan is Riot Games. The group claims they have access to the company’s backend servers.
In addition, the group has joined forces with REvil, a ransomware group that was linked to the Russian government in the past, and KillNet, another Russian threat group with relatively widespread resources, targeting US financial systems such as SWIFT, the US Federal Reserve System and other US-based organizations.
Hacktivists’ main pursuit is to relentlessly cause chaos and disruption. Their campaigns are often fueled by self-serving motives, with a primary focus on gaining public attention and garnering PR for themselves.
While they claim to be fighting for noble causes, their actions are primarily aimed at attracting media coverage and achieving a cult-like following.
The negative consequences of their hacking activities are often overlooked, as they exploit vulnerabilities in systems and expose sensitive information without considering the potential harm inflicted on innocent individuals.
Their approach disregards the principles of legality and undermines the proper channels for enacting change, resorting instead to cyber warfare and aggressive tactics. As their notoriety grows, so does their disregard for ethics, making it increasingly challenging to separate genuine activism from attention-seeking stunts.
Ultimately, the impact of hacktivists is overshadowed by their thirst for recognition, casting doubt on the authenticity of their intentions and the long-term benefits of their campaigns.
As the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to gain prominence across industries, it is important to understand and address the risks associated with employees using AI systems. By recognizing and mitigating these risks, organizations can effectively safeguard their operations, data, and reputation. Broadly speaking, the risks associated with employing AI in workplace machinery encompass the hazards of malicious AI utilizing malicious injections on employees, data breaches that compromise the security of customer or employee data, privacy violations, and the potential theft of intellectual property. When considering the United States specifically, there are additional risks that are particularly relevant and US-based companies should be aware of.
To protect personal and sensitive data, the United States has established specific regulations like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Companies must comply with these rules to avoid legal consequences and damage to their reputation. Additionally, since the US is a leading hub for technology, organizations should prioritize safeguarding their proprietary algorithms and trade secrets to minimize the risk of intellectual property disputes. Companies may face legal action, resulting in costly consequences and harm to their reputation if they fail to comply with regulations or if their AI systems cause privacy breaches or discriminatory actions.
The competitive nature of the US market demands strong measures to safeguard AI systems and the sensitive information they contain from unauthorized access or exploitation by competitors. Moreover, the US faces specific risks posed by sophisticated nation-state actors that already seek to infiltrate AI systems. These threat actors may attempt to gather intelligence, disrupt operations, or engage in cyber espionage. Given the economic and geopolitical prominence of the US, these risks can be particularly pronounced.
ChatGPT emerged in November 2022, swiftly becoming a remarkable AI tool renowned for generating human-like text responses based on prompts or conversational context. Its ability to comprehend and produce coherent and contextually relevant answers across a vast spectrum of inquiries and requests has made it extremely popular among businesses and individual users.
As of today, ChatGPT is the fastest-growing service in the history of the Internet, gaining a significant user base in a short time, and became increasingly popular among professionals and companies across a wide range of industries. Its rapid ascent in popularity has captivated professionals and companies across diverse industries, with an ever-expanding user base. Professionals and individuals alike are using ChatGPT to heighten their efficiency and productivity and have integrated this tool into their workflow, leveraging its capabilities to augment their respective fields.
Despite the numerous benefits associated with working with ChatGPT, it also provides a new path for threat actors’ malicious intentions and offers them a valuable tool for targeting and attacking their victims.
Cyberint’s analysis of the Argos malware log collection has revealed a significant number of 259,887 compromised ChatGPT accounts since the beginning of 2023.
Both private and corporate ChatGPT accounts are being sold by threat actors in dark web forums and marketplaces, where they serve as active platforms for such transactions. The highest bidder can acquire these compromised accounts easily.
Given that all conversations with ChatGPT are saved, if a threat actor manages to compromise a ChatGPT account, they could potentially gain access to the complete conversation history. This becomes a concern since many employees who use ChatGPT also share sensitive information while seeking assistance. Consequently, if a threat actor gains access to these compromised accounts, they can potentially obtain the company’s most sensitive information. This includes insights into employees, customers, secret projects, code development, and more.
Armed with harmful information extracted from the conversation history, the threat actor may then leak the company’s sensitive data and plan targeted attacks utilizing the acquired intelligence. They can employ social engineering techniques by familiarizing themselves with the company and its future plans, impersonating an employee, and potentially deceiving other employees or external contacts into revealing confidential information or engaging in unauthorized actions.
Furthermore, threat actors could exploit vulnerabilities or identify entry points based on the technologies or packages discovered through their exploration of the company’s activities in ChatGPT. Threat actors may also gain visibility into code snippets, discussions, and other sensitive information shared within the ChatGPT account. This could encompass proprietary code, credentials, API keys, or any other confidential data relevant to the company’s projects.
There is also a risk of intellectual property theft, as unique algorithms, ideas, and innovative solutions discussed or shared on ChatGPT could be stolen and used for the threat actor’s own purposes or be sold to competitors.
On March 15, the FBI arrested an individual suspected of being the notorious Pompompurin, the admin of one of the most popular cybercrime forums today − BreachForums.
The individual is 21-year-old Conor Brian Fitzpatrick, who federal agents claim admitted to being the famous Pompompurin. Pompompurin is a famous cybersecurity individual with whom everyone in the community is familiar.
BreachForums is still up and running and is currently managed by another admin named Baphomet.
The cyber security community already has mixed opinions about the reason for his arrest, the future of BreachForums, and how the freedom of Pompompurin depends on the people he is willing to take down with him.
Ruslan Magomedovich Astamirov has been arrested in Arizona and charged by the U.S. Justice Department for deploying LockBit ransomware on networks in multiple countries. If convicted, he could face up to 20 years in prison for wire fraud and up to five years for damaging protected computers.
The U.S. government is determined to expose ransomware perpetrators and bring them to justice, emphasizing that online anonymity will not protect them. Astamirov is the third individual to be prosecuted in connection with LockBit, following the arrests of Mikhail Vasiliev and the indictment of Mikhail Pavlovich Matveev.
Evidence suggests that Astamirov used specific email addresses and controlled an IP address involved in the attacks.
The U.S. is one of, if not the most, targeted region in the world.
As there are many opportunities, both financial and PR, threat actors of all kinds target this region, given the number of opportunities.
Although some impressive and high arrests were made recently by the FBI and other law authorities, there is no real indication of any decline in cybercrime activity.
As the bar to becoming a successful threat actor in the cybercrime industry gets lower, especially with the emergence of ChatGPT and other AI modules, the number of active threat actors grows massively by the day.
See the full webinar below:

©1994–2025 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved.
Copyright | Privacy Policy | Cookie Settings | Get the Latest News
Fill in your business email to start