The ransomware landscape is evolving with increased competition among threat groups and the emergence of new ransomware operations. However, victim organizations and potential targets are strengthening their security measures and procedures to prepare for potential ransomware attacks. Our latest quarterly report for Q1 2024 shows a significant decrease in ransomware incidents, down to 1,048 cases, representing a 22% decline compared to Q4 2023.
Recent law enforcement actions have disrupted major ransomware operations, including the arrest of LockBit affiliates, ALPHV pursued by the FBI, and actions against Ragnar Locker and others, shaking the foundations of the ransomware industry. Additionally, ransomware incident response firm Coveware reports a record low proportion of victims choosing to pay ransom in Q1 2024, highlighting a shift in victim response to ransom demands.
The Cyberint research team has identified a new trend in ransomware operations targeting smaller businesses with lower revenue over the past six months. This shift is evident in the decreasing revenue of victims targeted by ransomware attacks, particularly those falling below the median revenue threshold.
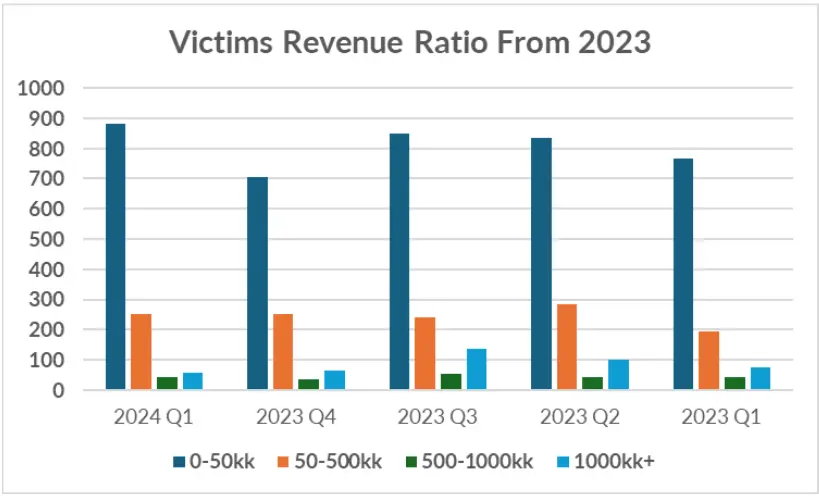
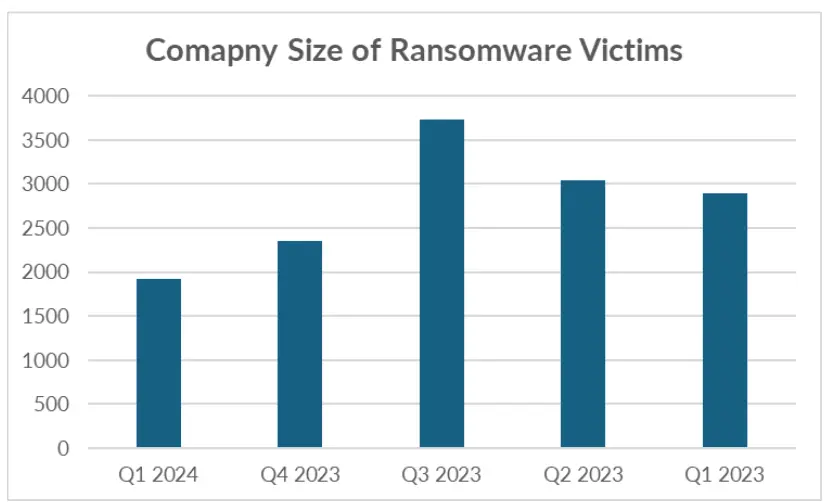
Analysis of victim revenue groups over five quarters reveals a sustained distribution, with more victims falling into lower revenue categories in recent quarters, contributing to the overall decrease in average victim revenue. The correlation between company size and revenue reinforces the observation that ransomware attacks are increasingly affecting smaller organizations with lower revenue.
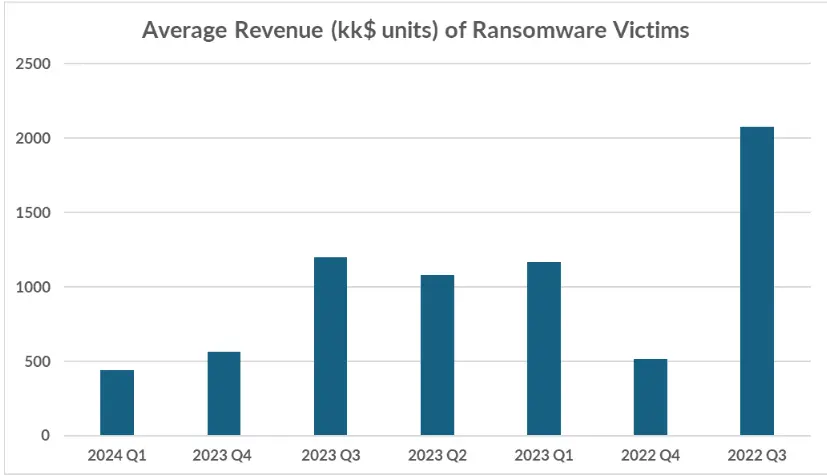
Furthermore, the number of victims with revenue exceeding $1 billion decreased by 53% from Q3 to Q4 2023, and by 11% from Q4 2023 to Q1 2024. These statistics contribute significantly to the declining average victim revenue during this period.
However, as depicted in the graph below, the distribution ratio among the divided groups remains consistent. What isn’t immediately evident from the graph is that the victims within each revenue group are closer to the lower revenue limit, explaining the significant decrease observed in the first graph.
Organizations impacted by ransomware attacks are increasingly self-sufficient in recovering from encryption breaches, reducing reliance on decryption keys. Despite ransom payments, stolen data often remains exposed or traded, highlighting the ineffectiveness of paying ransoms as a guarantee of protection.
Coveware, a ransomware incident response firm, has cited cases where LockBit retained stolen data from ransom-paying victims, while data from previous Hive victims surfaced on the Hunters International leak site. This underscores the limited effectiveness of ransom payments in preventing data leaks both immediately and in the long term.
Furthermore, in late 2023, forty countries led by the United States formed an alliance committing to never pay ransom to cybercriminals and to disrupt funding mechanisms for threat actors. These initiatives include enhanced information sharing on ransom payment accounts. Lithuania and Israel, along with the UAE, will establish information-sharing platforms to facilitate coordination, with partner countries sharing a “black list” through the U.S. Department of the Treasury containing details of digital wallets used for ransomware payments.
Recent law enforcement actions, including the apprehension of key ransomware affiliates and disruptions to major ransomware operations, have significantly impacted the ransomware industry. Notably, the proportion of victims opting to pay ransom reached a record low of 28% in Q1 2024, according to Coveware, highlighting a strategic shift away from ransom payments as a reliable solution.
Coveware’s latest report shows a continued decline in the average ransomware payment, reflecting evolving dynamics within the ransomware landscape.
As ransomware operations target smaller businesses with lower revenue, organizations must bolster their cybersecurity defenses to mitigate the risk of ransomware attacks. The relationship between company size, revenue, and ransomware impact underscores the evolving nature of ransomware threats and underscores the need for proactive cybersecurity measures to fend off ransomware incidents.
We anticipate that this trend will persist into Q2 of 2024 and may signify a fundamental shift in the ransomware industry. The proliferation of new groups on a daily basis, many of which are small-scale operations, underscores the varied motivations of threat actors focused on profiting from ransomware attacks.
©1994–2025 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved.
Copyright | Privacy Policy | Cookie Settings | Get the Latest News
Fill in your business email to start